Product Info Couplings (Shaft Couplings)
A coupling is a mechanical element used to connect the drive shaft and driven shaft and transmit the motor's power to the device.
Couplings also play a variety of roles in connecting the drive shaft and driven shaft, such as absorbing misalignment (mounting error) between the shafts, reducing motor vibration, preventing the transfer of motor heat to the device, and preventing breakdowns in the motor or device due to damage to the coupling in the event of some kind of problem.
table of contents
Coupling Related Information
What is a coupling (shaft coupling)?
- This is a part that connects the shaft (driver side) and the shaft (driven side).
A coupling is used to connect the shaft of a driving machine (such as a motor) and the shaft of a driven machine such as a pump, which are facing each other, and is also called a shaft coupling.
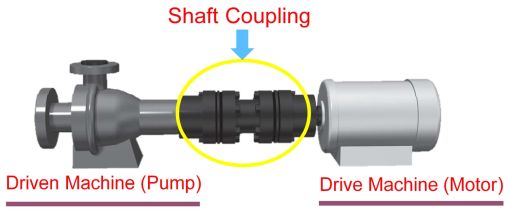
The role of couplings
Role 1: Transmits rotational force (torque) between in-line shafts.

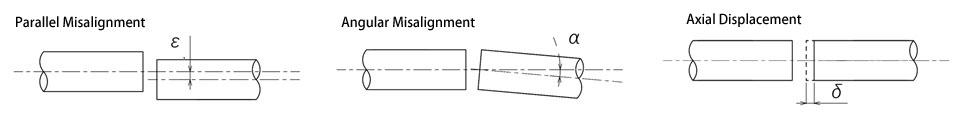
Role 2: Absorbs mounting errors (misalignment).
Coupling product list
Rigid Coupling (Power Rigid Coupling): Lightweight, low inertia, non-backlash, no lubrication
Rigid couplings are specialized for machine tool applications and have the highest torsional rigidity.
Although it has high torsional rigidity, it does not have any flexible elements and therefore cannot absorb misalignment.
Use only if reliable centering is possible.
(Not recommended for general use)
Power RigidCoupling
Model number EPR□□~
A rigid coupling for machine tools that achieves highly reliable fastening with a taper lock structure.
- ・Available in straight shaft and tapered shaft types:
Compatible with tapered shaft servo motors, and applies adapters for Φ11 tapered shaft and Φ16 tapered shaft. - ・High torsional rigidity:
The structure does not have flexible elements, so it has high rigidity. - ・Non-backlash:
The taper lock method uses frictional fastening, so there is no backlash. - ・Compact and low moment of inertia:
The axial length has been shortened to the limit, allowing for a compact design.
By using a polygonal shape, we have also achieved a reduction in the moment of inertia.
Applicable shaft diameter
Φ16mm~Φ48mm
Torque Range
78~489N・m


