Shock Guard TGF Series

- Highly accurate return position type
- - Preload is applied to the support bearing of the drive plate to eliminate gaps, and the mounting surface is polished to improve the accuracy of the output mounting surface.
If even greater runout accuracy is required, the mounting surface can be polished based on the hole after assembly to eliminate slight runout errors caused by assembly. - - Backlash is extremely small and the return position is highly accurate, making it ideal for indexers.
- - After removing the cause of the overload, simply rotate the drive side and the gears will automatically re-engage.
- - The arrangement of the balls and pockets that serve as torque transmission elements is a unique combination that only meshes in one place.
Structure
TGF20~45

(1) Hub (2) End nut (3) Hexagon socket head set screw (4) Drive plate (5) Slide plate (6) Adjustment nut
(7) Coil spring (8) Drive ball (steel ball A) (9) Snap ring (10) Hexagon socket set screw (11) Steel ball B (12) Steel ball C
(13) Housing (14) Thrust bearing (15) Hexagon socket set screw
TGF65~90

(1) Hub (2) End nut (3) Hexagon socket head set screw (4) Drive plate (5) Slide plate (6) Adjustment nut
(7) Spring holder (8) Hexagon socket head screw (9) Coil spring (10) Drive ball (steel ball A) (11) Bush
(12) Snap ring (13) Hexagon socket set screw (14) Radial bearing (15) Thrust bearing A
(16) Thrust bearing A (17) Housing (18) Thrust bearing B
Operating principle
Please watch the animation to see the operating principle of the TGF series.
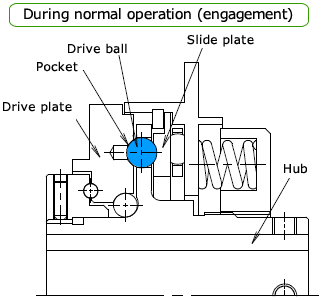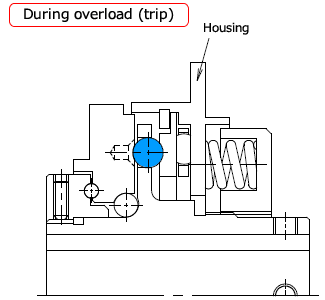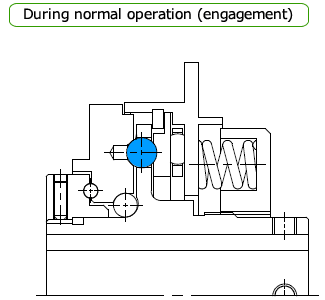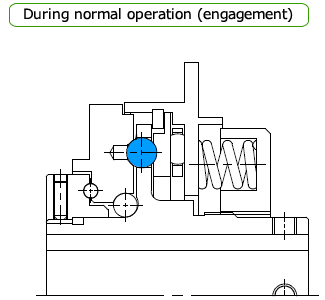
Normal (engaged)
Power for the TGF series enters through the hub and is transmitted to the drive plate on the output side via the drive balls (or vice versa).
Sprockets and Belt Sprockets are attached directly to this drive plate with bolts.
The hub flange has holes for the drive balls, and the drive balls are placed in these holes. The output drive plate has pockets for the drive balls.
Power is transmitted by pressurizing the drive ball with a coil spring through the thrust race.
When overloaded (tripped)
When an overload occurs, the drive ball pushes the thrust race up towards the coil spring, and the drive
It pops out of the pocket in the plate and cuts off power.
At this time, the cover moves toward the coil spring, and by detecting this amount of movement with a TG sensor or similar, it is easy to automatically stop the drive source after an overload occurs.
Reset method
After an overload, if you restart it, it will automatically return to its original position within one rotation.
The TGF series will continuously reset if rotation continues after operation, so after an overload occurs, detect the overload with a TG sensor or similar and immediately stop the drive source.
Specifications (standard model)
| Set torque range N・m | Repeated operating torque accuracy | Backlash | Reset method |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6.0~4900 | ±5% | Extremely small | Automatic |
■Type 2: Belt Sprockets, etc. can be directly attached. Shaft setscrews can be tightened externally.
■Type 3: Thinner than Type 2, ideal for attaching Power-Lock. (See the link for details.)
■Type 5: A coupling type that combines ECHT-FLEX to allow for angle errors.
■Type 7: A coupling type that combines ECHT-FLEX, allowing for errors in angle and parallelism.
Catalogs and Instruction Manuals
Model number display
*Single unit type
| TGF | 20 | - | L | 2 | - | TH20JD2 | - | N19 |
| | Series |
| Size |
| | | | |
| type 2: Type 2 3: Type 3 |
| Shaft hole symbol |
| Torque setting value N・m |
|||
| Spring strength L: Weak spring M: Medium spring H: Strong spring |
||||||||
*Coupling type
| TGF | 20 | - | L | 5 | - | TH20PD2 | X | CH30PD2 | - | N18 |
| | Series |
| Size |
| | | | |
| type 5: Type 5 7: Type 7 |
| Shock Guard side Shaft hole symbol |
| Coupling side Shaft hole symbol |
| Torque setting value N・m |
||||
| Spring strength | ||||||||||
Note) The position of the setscrew on Shock Guard side is the position seen from the adjustment nut side, and the position of the setscrew on the coupling side is the position seen from the hub end face.
■ Tsubaki model No. navigation
Product model number list
*Click on the model number to display detailed information.
| Set torque range N・m |
Single unit | Coupling Type | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shaft hole diameter range mm |
Model number | Coupling side Shaft hole diameter range mm |
Model number | |||
| Type 2 | Type 3 | Type 5 | Type 7 | |||
| 6.0~20 | 10~20 | TGF20-L2 | TGF20-L3 | 17~42 | TGF20-L5 | TGF20-L7 |
| 12~40 | TGF20-M2 | TGF20-M3 | TGF20-M5 | TGF20-M7 | ||
| 24~80 | TGF20-H2 | TGF20-H3 | TGF20-H5 | TGF20-H7 | ||
| 10~74 | 12~30 | TGF30-L2 | TGF30-L3 | 17~60 | TGF30-L5 | TGF30-L7 |
| 20~147 | TGF30-M2 | TGF30-M3 | TGF30-M5 | TGF30-M7 | ||
| 40~294 | TGF30-H2 | TGF30-H3 | TGF30-H5 | TGF30-H7 | ||
| 30~156 | 22~45 | TGF45-L2 | TGF45-L3 | 27~74 | TGF45-L5 | TGF45-L7 |
| 60~313 | TGF45-M2 | TGF45-M3 | TGF45-M5 | TGF45-M7 | ||
| 120~568 | TGF45-H2 | TGF45-H3 | TGF45-H5 | TGF45-H7 | ||
| 50~269 | 32~65 | TGF65-L2 | TGF65-L3 | 47~95 | TGF65-L5 | TGF65-L7 |
| 100~539 | TGF65-M2 | TGF65-M3 | TGF65-M5 | TGF65-M7 | ||
| 200~1078 | TGF65-H2 | TGF65-H3 | TGF65-H5 | TGF65-H7 | ||
| 300~1225 | 47~90 | TGF90-L2 | TGF90-L3 | 52~118 | TGF90-L5 | TGF90-L7 |
| 600~2450 | TGF90-M2 | TGF90-M3 | TGF90-M5 | TGF90-M7 | ||
| 1200~4900 | TGF90-H2 | TGF90-H3 | TGF90-H5 | TGF90-H7 | ||
option
TG sensor
This is a proximity switch type overload detection sensor designed specifically for Shock Guard. It can detect an overload on Shock Guard (movement of the plate in the axial direction) and stop the motor or issue an alarm.

| AC type | DC type | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Model number | TGS8 | TGS8DN | |
| power supply Voltage |
Rating | AC24~240V | - |
| Usable range | AC20~264V(50/60Hz) | DC10~30V | |
| Current consumption | 1.7mA or less (at AC200V) | 16mA or less | |
| Control output (switching capacity) | 5~100mA | Max 200mA | |
| indicator light | Operation display | ||
| Ambient temperature | -25 to +70°C (but do not freeze) | ||
| Ambient humidity | 35~95% RH | ||
| Output format | - | NPN | |
| Operation form | NC (センサプレートを検知していない時の出力開閉状態を表します) |
||
| Insulation resistance | 50MΩ or more (DC500V megger) between all live parts and case | ||
| mass | Approximately 45g (2m cord length) | Approximately 56g (2m cord length) | |
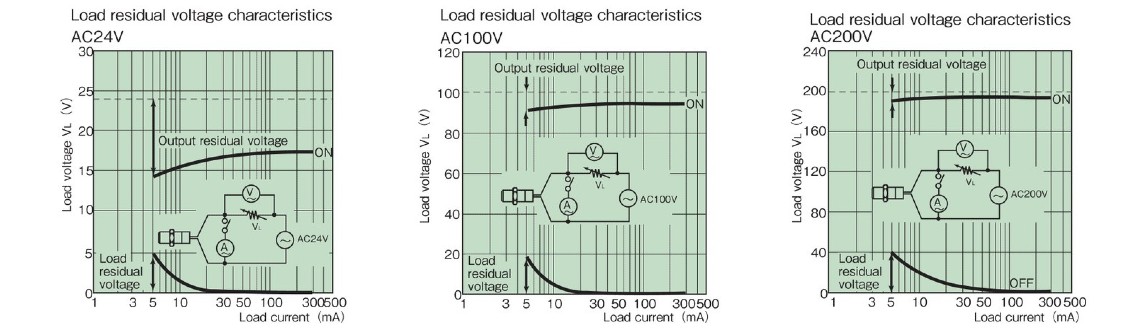
| Residual voltage | >> See characteristic data | 2.0V or less (load current 200mA, cord length 2m) | |
| Instruction Manuals | TG sensor TGS8 | TG sensor TGS8DN | |
Load residual voltage characteristics
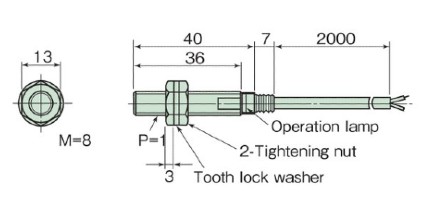
Dimensions
AC type TGS8
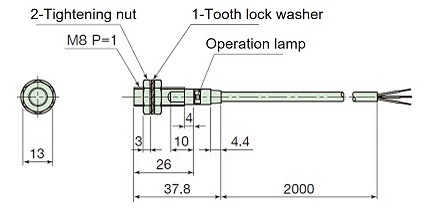
DC type TGS8DN
Sizing
We will select Shock Guard that best suits your usage conditions from the entire Tsubaki Shock Guard series.
Please click on the "sizing" tab at the top of this page.
Back to top of this pageTorque adjustment
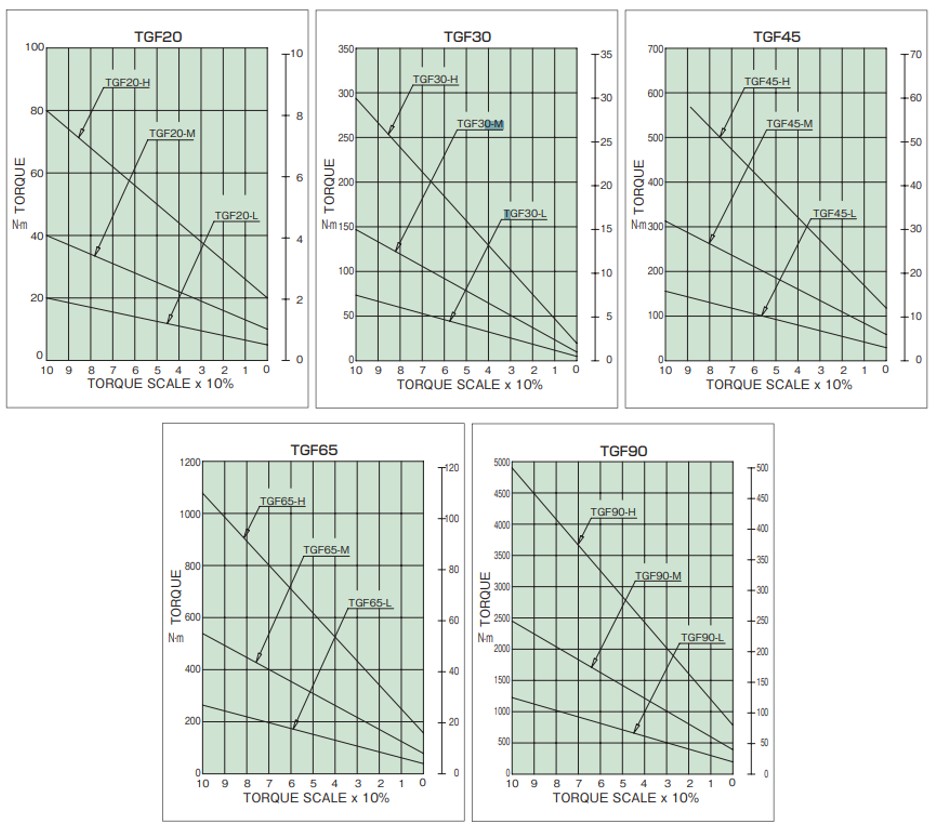
1. Read the torque scale value that corresponds to the required torque from the torque correlation diagram, and tighten the adjustment nut to this value.
To tighten the adjustment nut, insert a hook wrench or round bar into the hole on the outside of the nut and turn it.
(Note) If the required torque is high (200 N m or more) for the TGF30 and 45 sizes, use the dedicated hook wrench (sold separately).
If the required torque is high for TGF65 and 90 sizes, loosen the bolt and tighten the adjusting nut with the hexagon socket set screw until the required torque scale is reached, then tighten the bolt completely.
Torque can be easily adjusted by tightening.

⇐ Torque scale
The torque of the product does not necessarily match the correlation diagram below, so please use it as a guide.
2. Once the torque has been determined, add the value to the nameplate, so that even if the product is disassembled for maintenance, it can be easily returned to the previous set torque.
In addition, you can make the reproduction more accurate by stamping a match mark on the end face of the hub on the nut.
Torque correlation diagram