Troubleshooting Large size conveyor chain
General
Plate related
Pin Related
| 18 | (1) Fatigue failure of the pin |
|---|---|
| 19 | (2) Corrosion fatigue of pins |
| 20 | (3) Brittle fracture of the pin |
| 21 | (4) Rapid pin destruction |
Bush and roller related
| 22 | Roller rotation failure Roller is unevenly worn |
|---|---|
| 23 | The roller opens. |
| 24 | Rollers and bushings break. |
| 25 | The rollers wear out in a drum shape. |

General
| 1 |
|---|
| Cause 1 | Chain and sprocket are not compatible | Solution | Replace the chain or sprocket with the correct size. Install a tensioner. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cause 2 | Insufficient winding angle | Solution | The winding angle shall be 3 teeth or more. |
| Cause 3 | Significant overload | Solution | Reduce the load (e.g., by adding a shock absorber). |
| Cause 4 | Insufficient back tension | Solution | Adjust the catenary, take-up, and install the tensioner. |
| Cause 5 | The chain is worn and stretched. | Solution | Replace with a new chain. |
| Cause 6 | The center distance between the chain and sprocket is not compatible. S≠S' | Solution | After inspection, make corrections. |
| 2 | The chain gets wrapped around the sprocket (it is difficult to disengage). |
|---|
| Cause 1 | There is too much chain slack. | Solution | Adjust the chain length or center distance, or install a tensioner. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cause 2 | Sprocket wear Chain and sprocket mismatch | Solution | Replace the chain and sprockets with new ones. |
| 3 | There is a strange noise. |
|---|
| Cause 1 | Insufficient oil supply to the sliding parts of the pin/bush | Solution | Lubricate sufficiently. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cause 2 | Insufficient oil supply to the bushing/roller sliding area | Solution | Use bearing rollers and Plastic Roller. |
| Cause 3 | Entanglement and running over | Solution | As mentioned above |
| Cause 4 | Loose chain casing or bearing | Solution | Retighten all bolts and nuts. |
| Cause 5 | Interference between the chain or moving part and the casing | Solution | After inspection, make corrections. |
| Cause 6 | Significant wear on the chain or sprockets | Solution | Replace the chain or sprockets (replace the entire chain). |
| Cause 7 |
Guide channel setting error |
Solution | After inspection, make corrections. |
| 4 |
|---|
| Cause 1 | Sprocket misalignment | Solution | Remove the chain and correct the centering of the drive and driven sprockets. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cause 2 | The chain is pushed sideways. | Solution | Eliminate the cause of the pressure. Use guide rollers. |
| Cause 3 | Runout due to poor machining accuracy of sprocket shaft hole | Solution | After checking for defects, correct them and replace with a new sprocket. |
| 5 | Wear of sprocket tooth root and tooth bearing surface |
|---|
| Cause 1 | Chain wear | Solution | Replace the chain and sprockets at the same time. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cause 2 | Insufficient number of meshing teeth | Solution | Increase the number of teeth on the sprocket. |
| Cause 3 | Uses BF chain (without rollers) | Solution | Change to RF chain (with rollers). |
| Cause 4 | Wear inclusions and insufficient hardness of the teeth against excessive load | Solution | Use hardened tooth tips or block replacement teeth. |
| Cause 5 | Incompatible sprocket and chain | Solution | Replace the chain or sprocket with the correct size. |
| 6 | Poor articulation |
|---|
| Cause 1 | Rusty and corroded | Solution |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Cause 2 | The conveyed object is stuck between the pin/bush/plate, or foreign matter gets in. | Solution |
|
| Cause 3 | Chain deformation due to improper installation | Solution | Check and correct the installation of the sprocket and shaft. |
| Cause 4 | Insufficient lubrication | Solution | Consider using oil or wear-resistant specifications (CT, BT Series, etc.). |
| Cause 5 | Use at high temperatures (over 400°C) | Solution | Use a chain with the appropriate clearance. |
| Cause 6 | Burnout due to overload | Solution | Reduce the load. Oil regularly (for example, by installing an oiling device). |
| Cause 7 | Pin bending due to severe overload | Solution | Reduce the load. Oil regularly (for example, by installing an oiling device). |
| 7 | The chain sticks and slips (stick-slip phenomenon). |
|---|
| Cause 1 | Change the chain's rolling friction coefficient. | Solution |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Cause 2 | It's slow. | Solution | Make it faster than it is now. |
| Cause 3 | The frame is not rigid enough, and the chain is small compared to the device. | Solution |
|
| Cause 4 | Increased friction | Solution |
|
| Cause 5 | conveyor length is long. | Solution | Divide the conveyor to shorten conveyor length. |
| Cause 6 | Speed fluctuation due to polygonal movement | Solution | The number of teeth on the drive sprocket must be 12T or more. |
| 8 | One of the Inner link or pins of an NF block chain or BF chain (without rollers) wears out. |
|---|
| Cause 1 | Internal tension increases when meshing with the sprocket. | Solution |
|---|
| 9 | Chain rust |
|---|
| Cause 1 | Inappropriate material selection | Solution | Replace the chain. Protect from the atmosphere. Apply anti-rust agent. (Oil, cover) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cause 2 | condensation | Solution | Eliminate the temperature difference between the inside and outside of the conveyor (using heat insulation, etc.). Install a drain to remove water. |
| 10 |
|---|
| Cause 1 | Abrasive materials such as ore powder can adhere to the chain, causing wear on the chain surface. | Solution |
|
|---|
| 11 |
|---|
| Cause 1 | Acidic and alkaline liquids cause corrosion, and mechanical wear is also added to this, accelerating wear. | Solution |
|
|---|
| 12 |
|---|
| Cause 1 | When a chain is covered with water or passes through a solution, the sliding parts of the chain form a local battery, causing galvanic corrosion of the surface. | Solution |
|
|---|
Plate related
| 13 | Rapid plate fracture |
|---|
| Cause 1 | Excessive load, excessive take-up tension | Solution |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Cause 2 | Strength reduction due to wear and corrosion | Solution |
|
| Cause 3 | Solution |
|
|
| 14 | Deformed plate holes, pin rotation (pin is out of position) |
|---|
| Cause 1 | overload | Solution |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Cause 2 | Improper assembly of connecting link | Solution | Replace the joint with a new one. |
| Cause 3 | Overload and poor lubrication | Solution | Replace with a new one. Improve overload and oil supply. |
| Cause 4 | Sticking between pin and bush, poor bending | Solution |
|
| 15 |
|---|
| Cause 1 | Overload, excessive tension on take-up, excessive repeated load | Solution | Excluding overload and excessive repeated load. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cause 2 | A load exceeding Maximum allowable load is applied. | Solution |
|
| Cause 3 | Repeated loads are applied to the attachment | Solution |
|
| 16 |
|---|
| Cause 1 | Use in acidic or alkaline environments Not the effect of repeated loading |
Solution |
|
|---|
| 17 | Red patterns are visible on the plate |
|---|
| Cause 1 | Scale adhering to the plate material | Solution |
|
|---|
Pin Related
| 18 |
|---|
| Cause 1 |
If a load exceeding Maximum allowable load is repeatedly applied, the pin may be subject to fatigue failure. The peak load acts as a cyclic load on the chain. |
Solution |
|
|---|
| 19 | (2) Corrosion fatigue of pins |
|---|
| Cause 1 |
The side with the pit is subjected to a tensile load, causing destruction to progress from the pit. In particular, if the surface of the pin is corroded, it becomes weak against bending, making this phenomenon more likely to occur. |
Solution |
|
|---|
| 20 | (3) Brittle fracture of the pin |
|---|
| Cause 1 |
Environmental factors |
Solution |
|
|---|
| 21 | (4) Rapid pin destruction |
|---|
| Cause 1 |
overload |
Solution |
|
|---|
Roller Bush Relationship
| 22 | Roller rotation failure Roller is unevenly worn |
|---|
| Cause 1 |
Roller load is excessive |
Solution | Use proper lubrication between bushings and rollers and appropriate specifications (DTA, bearing rollers, etc.). |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cause 2 |
Conveyed objects and foreign matter get between the bush and roller. |
Solution | Remove regularly and install a partition to protect the chain. |
| Cause 3 |
Transported materials and foreign matter accumulate on the rails |
Solution | Regularly remove the waste and install partitions to prevent accumulation. |
| Cause 4 |
Lubricant does not get between the bush and roller or between the roller and plate |
Solution | Select the appropriate lubricant and lubrication method. |
| Cause 5 |
Rusted bushings and rollers |
Solution | Select the appropriate specifications (RT, etc.). |
| Cause 6 |
The inner plate moves inward. |
Solution | Replace, re-inspect installation, and check load. |
| Cause 7 |
Bush crack |
Solution | Reduce the load and reduce the rotation speed. |
| Cause 8 |
Contact between roller side and plate side due to thrust load |
Solution | Excluding thrust load factors. |
| Cause 9 |
Incompatible chains and sprockets, worn teeth |
Solution | Check the tooth profile. |
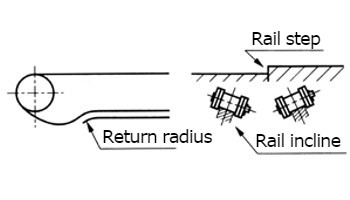
| 23 | The roller opens. |
|---|
| Cause 1 |
Overload, excessive take-up tension |
Solution | Reduce the load, lubricate properly, and remove excessive rail steps. Loosen the take-up. |
|---|
| 24 | Rollers and bushings break. |
|---|
| Cause 1 |
Overload, excessive take-up tension |
Solution | Reduce the load. Properly lubricate. Loosen the take-up. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cause 2 |
Too few teeth for the speed. |
Solution | Increase the number of teeth. Reduce the speed. |
| 25 | The rollers wear out in a drum shape. |
|---|
| Cause 1 |
Overloaded or under-lubricated |
Solution | Check for overload or improve oil supply, or replace the chain with a new one. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cause 2 |
Rail wear |
Solution | Repair or replace rails. |