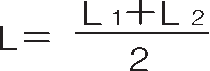Q&A Drive chain
We have posted frequently asked questions from customers in Q&A format. Please click on the question to proceed to the answer.
Words in Q&Aof
Drive chain
Chain peripherals

| Q1 | What are the product lineup and features of stainless Drive chain? | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 |
Stainless steel is generally a material with excellent corrosion resistance, chemical resistance, and heat resistance. Tsubakimoto Chain offers the following types of products that take advantage of the advantages of stainless steel, and these products are used in a variety of industries and applications, primarily in the food machinery industry.
*We also offer Poly-steel chains that use plastic for inner links and stainless steel for outer links, and are lube-free, lightweight, and quiet. Back to Questions |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q2 | What is the difference between NP Series and NEP Series Surface treated drive chain and when should you use them? | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A2 |
Stainless steel Drive chain are more corrosion resistant than steel chains, but their strength (Maximum allowable load) is less than 1/8. For applications that require strength on a par with steel chains and excellent corrosion resistance, Surface treated drive chain with NP Series and NEP Series are used. (However, they do not have the corrosion resistance of stainless steel Drive chain.)
*Strength ratio is an approximate value with steel being 100. Back to Questions |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
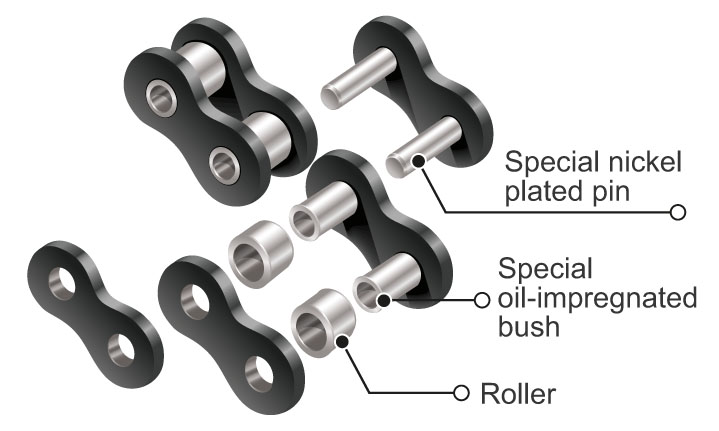
| Q3 | What is a Lambda Chain? | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A3 |
Lubrication is essential to prevent wear and tear on chains and extend their lifespan.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q4 | Can you manufacture multiple strand Lambda Chain? | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A4 |
When Lambda Chain was first released, it was only available as single strand. Subsequently, due to numerous requests for a double-strand chain, it was added to the catalog and commercialized in 2001. However, please note that the dimensions, transmission capacity, and Maximum allowable load differ from those of RS roller chain.
*Three or more strands cannot be manufactured with Lambda Chain due to performance issues. Back to Questions |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q5 | Is it okay to oil Lambda Chain? | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A5 |
Generally, Lambda Chain are ideal for applications where lubrication is not desired or possible. If regular lubrication is possible RS roller chain can be expected to have a longer lifespan, so we recommend RS roller chain. (Even with Lambda Chain, proper lubrication can further extend their lifespan, as shown in the diagram below.)
<Lubrication instructions> ・Lubrication cycle Because the bushings are originally oil-impregnated, the interval between initial oiling can be longer compared to RS roller chain, etc. (However, the lubrication cycle from the second time onwards is the same as RS roller chain, etc.) The most effective time to oil is before the chain begins to stretch rapidly (point A) in the diagram above; oiling after stretching has begun will not significantly extend the chain's lifespan. When brown wear debris appears between the plates, the bushings have already run out of oil. Although this will vary depending on the conditions of use, as a guideline, oiling should be done every 1 to 3 days. ・Oil type Mineral or synthetic oils are fine, and extreme pressure hydraulic or gear oils are recommended. ·Viscosity It depends on the conditions of use, but a general guideline is around ISO VG68 to 220. <New product introduction> We have commercialized a long-life Lambda Chain that has an even longer lifespan than the conventional Lambda Chain. Back to Questions |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q6 | Which chains can be used in low temperatures? | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A6 |
When using the chain in low temperatures, such as in a freezer,
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
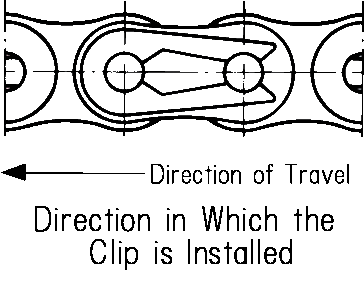
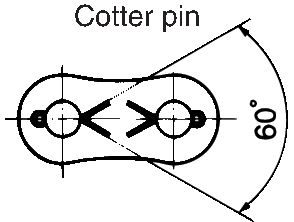
| Q7 | What is the installation direction for connecting link spring clip and cotter pins? | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A7 |
spring clip are used for connecting links on small roller chains below RS60. As shown in the diagram on the left, install with the head side facing forward in the direction of travel. When installing, be careful not to open the legs of spring clip too much.
RS80 to RS200 and small roller chains with 3 or more strands use cotter pins in the connecting links. As shown in the diagram on the left, insert the cotter pin from the outside and open the legs by about 60 degrees. Do not reuse cotter pins or use commercially available cotter pins. *The method of attaching connecting links varies depending on the chain type. Please refer to the catalog for details. Back to Questions |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q8 | What kind of lubricant should I use on my chain? | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A8 |
Lubrication is extremely important in roller chain transmissions.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q9 | Is grease effective for lubricating drive roller chains? | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A9 |
Chain wear occurs between the pin and bushing (resulting in pitch elongation), between the bushing and roller, between the outer plate and inner plate, and between the sprocket and roller. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q10 | What is the wear life limit of a chain? | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A10 |
(1) RS roller chain
When the chain articulate on the sprocket, the pins and bushes slide against each other, gradually causing wear on the outer periphery of the pin and the inner periphery of the bush. This causes the chain to elongate due to wear. As the chain elongates due to wear, it starts to climb up the ridges of the sprocket teeth, eventually causing tooth skipping and making it impossible to mesh.
(2) Lambda Chain The standard lifespan for Lambda Chain and Long Life Lambda Chain is approximately 0.5%. Unlike RS roller chain, these are used Lube-free, so replacement is required when the oil-impregnated sintered bushings run out of oil. This occurs when the elongation is approximately 0.5%. When the oil runs out, red wear debris will form between the plates and poor bending will occur, so use this as a guide for replacement.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q11 | What is the initial stretch of the chain? | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A11 |
After starting operation, chains elongate rapidly due to assembly distortion and initial break-in. This is called initial elongation, and elongation progresses more gradually thereafter. Initial elongation is normally around 0.1%, but most of our steel roller chains have initial elongation of 0.05% or less due to improved component precision and preloading after assembly. Back to Questions |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q12 | When should I use a chain tensioner? | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A12 |
(1) Main use cases Excessive chain slack can cause chain vibration and noise, shorten the lifespan of both the chain and sprocket, cause tooth skipping, and in some cases lead to unexpected problems. A tensioner is used to prevent this. By adjusting the tensioner to an appropriate level and being careful not to overtighten it, the chain's power transmission function can be maintained for a long period of time.
(2) Precautions for use 1. Generally, the tensioner should be placed on the slack side of the chain. If forward and reverse operation is frequent, it is necessary to place it on both sides. In this case, please note that an overload will be applied to the tensioner. If you would like to use our chain tensioner, please consult us. 2. Placing the chain closer to the sprocket rather than the center of the span allows for a larger adjustment amount with a small movement. Generally, it is placed on the outside of the chain near the small sprocket. This also ensures the proper wrapping angle for the small sprocket. 3. When pressing with the tensioner, be careful not to let the chains come into contact with each other. The chain will pulsate, especially during operation, so adjust with some slack. 4. Make sure that the tensioner sprocket has at least three teeth that mesh together. 5. Generally, we recommend that the tensioner sprocket have the same number of teeth as the small sprocket. Back to Questions |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q13 | How can I deal with chain noise? | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A13 |
When the chain engages with the sprocket, noise is always generated. The noise is generated from the following points: <Location of occurrence> 1. The impact noise that occurs when the roller (of the chain) hits the sprocket's tooth root. <Measures> A. Reduces collision energy. - Reduce the chain speed. - Increase the number of sprocket teeth. - Use a smaller chain to reduce mass. B. Provide a cushioning effect at the collision point. - Lubricate the tooth roots of the sprocket teeth and the gaps in each part of the chain (between plates, between pins and bushes, and between bushes and rollers). ・Use engineering plastic rollers (transmission capacity will decrease). - A low-noise Drive chain with spring rollers is used. Compared to RS roller chain (pre-lubed), noise levels are 6 to 8 dB lower (based on in-house testing). Back to Questions |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q14 | Why is the Maximum allowable load of stainless steel chains so low? | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A14 |
Maximum allowable load of stainless steel chains is approximately 1/8 that of steel chains. This is because allowable tension is set differently as shown below. RS roller chain (steel) Stainless Steel Drive chain (SS Series)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
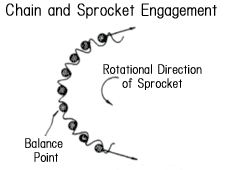
| Q15 | What causes uneven sprocket rotation and how can you fix it? | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A15 |
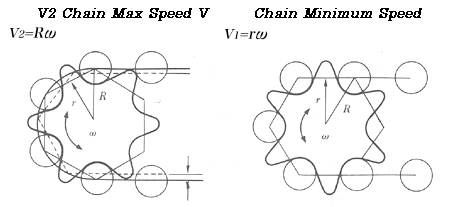
<Chain speed fluctuations> First, we will explain chain speed fluctuation, which is one of the causes of rotation unevenness. The chain meshes with the sprocket in a polygonal manner. Therefore, as shown in the diagram below, the height of meshing (radius from the center of the sprocket) is different when meshing at the tangent position of a circle and when meshing at the chord position. As a result, even if the drive sprocket rotates at a constant speed, the chain's traveling speed will vary by the radius ratio. The speed fluctuation rate is calculated using the following formula.
<Uneven rotation> Chain speed fluctuations and the properties of the sprocket cause rotational irregularities in the driven sprocket.Additionally, eccentric mounting errors in the sprocket and manufacturing errors in the chain and sprocket also have an effect.Increasing the number of teeth on the drive sprocket (using a larger diameter) will result in smoother transmission and less rotational irregularities. Back to Questions |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q16 | What is pin gear drive? | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A16 |
To make things move in a linear or rotary manner, roller chains or gears are generally used, passing through a reducer from a driving source (such as a motor).
Based on the table above, pin gear drives are ideal for:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q17 | What is the elastic elongation of roller chains and Lambda Chain? | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A17 |
RS roller chain single strand Please refer to the table below as a standard guideline.
Lambda Chain single strand
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q18 | What is the drive system for multi-roll (roller conveyors) and what are their features? | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A18 |
Multi-roll (roller conveyors) can be driven by a single motor or a line shaft, but here we will introduce three common drive methods that use chains. (1) Parallel hanging type 〇Method Advantages 〇Disadvantages 
(2) Rack type 〇Method Advantages 〇Disadvantages 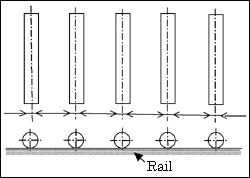
(3) Cross chain drive 〇Method Advantages 〇Disadvantages 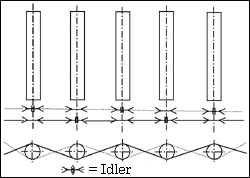
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q19 | What are the standards for chains? | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A19 |
Chains are mechanical components used in a wide variety of applications, and to ensure performance and compatibility, international and national standards have been established. Some of these standards are listed below (as of January 2007).
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q20 | Does the chain comply with the RoHS directive? | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A20 |
Tsubakimoto Chain's transmission and conveyor chains are all RoHS compliant. What is the RoHS Directive?
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q21 | What are the types of offset links (OL) and how do I order them? | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A21 |
If you are making a chain with an odd number of links, you will need an offset link (half link). (1) Types of offset links (OL)
(2) Points to note when arranging 2POL and 4POL Formation when you want to use 2POL with a total length of 9 links Example: Using MCJL and 2POL, total length 9L 
Formation for when you want to use 4POL with a total length of 11 links Example: When using FSJL and 4POL, total length 11L  Back to Questions
Back to Questions
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q22 | Is lubrication required when assembling connecting links (JL, OL, 2POL)? | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A22 |
Unless the connecting link is shipped assembled into the main body, it is usually shipped with only a light anti-rust oil applied. This is because applying lubricant with the same viscosity as the main body to the connecting link may reduce workability when the customer cuts or connects it. If the connecting link is used in the condition it was shipped in, it may wear out early due to insufficient lubrication. When assembling the connecting link into the main body, be sure to apply lubricant to the pin and bushing before assembling it into the main body. For 2POLs where the pin and bushing are already assembled, lubricate them as shown in the diagram below. *2POL lubrication position  Back to Questions
Back to Questions
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q23 | Has the name of a roller chain (Drive chain) ever changed in the past? | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A23 |
The names used to indicate roller chain sizes have not changed significantly since 1966. However, new product names may be added due to expansion of specifications and the lineup, so please check each product page. Although the current product has the same shape as the original product, its performance has been significantly improved. Please contact us for the design documents from that time or if you would like to replace it.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q24 | What is the difference between F-type connecting links and M-type connecting links? | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A24 |
connecting link plate The difference is whether the pin hole and pin of slip fit or press fit M-type connecting link: slip fit F-type connecting link: press fit ・Connecting and detaching work for maintenance can be done smoothly. ・For transmission where there is a risk of side force acting, 
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q25 | What precautions should I take when using a chain tensioner (made by Tsubakimoto)? | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A25 |
(1) When the chain pulsates, the tensioner rod moves in and out in reaction, sliding against the main body. This accelerates wear on the rod and main body, so please lubricate them during this time. (2) The tensioner will be severely damaged in a dusty or corrosive environment. Avoid using it in such an environment. (3) Avoid using the tensioner in cases where a thrust force is applied to it, such as in vertical drive, and where severe load fluctuations are applied, such as in forward and reverse operation, as this may cause severe damage to the tensioner. Back to Questions |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q26 | What is the relationship between chain tensioner displacement and pressing force? | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A26 |
The Tsubaki chain tensioner has two built-in coil springs in its main body, and the elasticity of these coil springs is used by the idler sprocket or plastic shoe attached to the end to press against the chain, adjusting the slack. Below is the formula for the relationship between the displacement of the idler sprocket or plastic shoe and the pressing force acting at that time. Please use this as a guide when installing and adjusting. ◆TCS type (swing type) ・Applied pressing force F(kN) 〇CT-TCS40, CT-TCS50 〇CT-TCS60, CT-TCS80 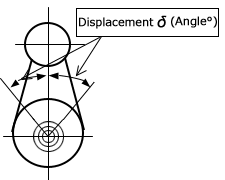
◆ETS type and TA type (direct acting type) ・Applied pressing force F(kN) 〇CT-ETS40, CT-ETS50, CT-TA40 〇CT-ETS60, CT-ETS80, CT-TA50, CT-TA60 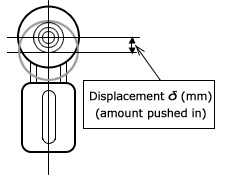
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q27 | Can the automatic roller chain lubricator (SFM68) be used facing upward? | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A27 |
When using the optional brush on the roller chain lubricator (SFM68), if it is installed facing upwards, the oil will not reach the tip of the brush. Use it facing downwards rather than horizontally. If you are not using a brush and are installing the piping, the layout is free for the orientation of the lubricator body, such as facing downwards, upwards, or sideways. However, the length of the piping must be less than 0.5 m, the inside diameter must be at least 6 mm, and the route must not be divided. Back to Questions |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q28 | What is the food machinery oil filled in the automatic roller chain lubricator (SFM68)? | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A28 |
The lubricant filled in the roller chain lubricator (SFM68) meets the FDA (U.S. Food and Drug Administration) Federal Regulations 21 CFR 178.3570*1 and has been H1*2 certified by the NSF (U.S. National Public Health Foundation), and is a lubricant whose safety has been confirmed. It contributes to "improving safety" in your product liability measures and HACCP*3 systems. 〇Safety Lubricant performance (lubricity, extreme pressure, heat resistance, oxidation stability, rust prevention, etc.) *1 Lubricants that accidentally come into contact with food are classified as "indirect food additives," and as a result of rigorous safety testing, the substances that may be used to make lubricants and their allowable concentrations are specified in detail. *2 Food machinery lubricants made from FDA-approved ingredients and certified as "usable for lubrication points that may accidentally come into contact with food." In addition to H1, there is also H2, which is considered "a lubricant that is not likely to come into contact with food, but is recommended for use in food factories." In other words, it cannot be used in places where it may come into contact with food. *3 HACCP is an abbreviation for Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point, which is a safety and hygiene management method. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q29 | Can the automatic roller chain lubricator (SFM68) be turned on and off frequently? | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A29 |
The gas generator (battery-powered gas generator), which is the switch for the roller chain lubricator (SFM68), can be turned on and off. [The gas generator has a lifespan of three years from the date of manufacture. If the machine will be stopped for an extended period of time, please be careful not to exceed this lifespan. Details are given in the catalog and Instruction Manuals.] Back to Questions |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q30 | Is there an easy way to measure chain wear elongation? | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A30 |
Normally, to measure chain wear elongation, you would use a vernier caliper or a tape measure to check the amount of elongation. For RS Roller Chains, BS Roller Chains, and Leaf Chains, we have a commercially available "chain wear measurement scale" that allows you to easily determine whether the chain has reached the end of its life. (The amount of elongation cannot be measured.) Back to Questions |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q31 | Can you handle special end bolts? | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A31 |
The end bolts, End fixture for use in hanging applications, are available in sizes RS40EB to RS120EB in the catalog. However, we can also accommodate special orders for other sizes upon request. Please contact us for details. Back to Questions |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q32 | Is there a simple tool for disassembling a chain? | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A32 |
Disassembly of a chain can be done with standard tools, provided you have a grinder, vise, and punch. We also offer chain-specific disassembly tools that are easier to use and more convenient. For more information, please see Drive Chain Accessories page. Back to Questions |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q33 | What is the direction of the load on the end bolt? | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A33 |
When using the roller chain horizontally (for trolley towing, pin gears, etc.) or vertically (for hanging, etc.), make sure that the load of the roller chain is applied to the center of the end bolt. Never use the roller chain in a way that causes the direction of the load acting on the center of the end bolt to differ from that of the roller chain (such as when a bending load is applied) or when a torsional load is applied. For other usage precautions, please refer to the usage precautions listed in the catalog. 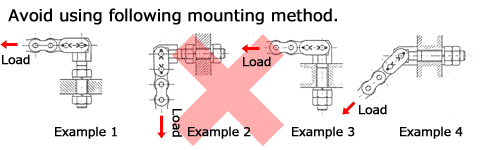 Back to Questions
Back to Questions
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q34 | How do I center the sprocket? | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A34 |
The quality of sprocket installation not only affects the smooth transmission and transport of the chain, but also determines the lifespan of the chain and sprocket. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 good
good