Q&A Sprocket
We have posted frequently asked questions from customers in Q&A format. Please click on the question to proceed to the answer.
Words in Q&Aof
Sprockets in general
RS sprockets for Drive chain
Small size conveyor chain sprockets
Large size conveyor chain sprockets

| Q1 | How should I consider when selecting a sprocket? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 |
The sprocket must be selected taking into consideration the model number and specifications of the chain to be used. The basic steps are as follows:
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q2 | What are the main materials used for sprockets? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A2 |
The main sprocket materials we use are listed in the table below. Products listed in the catalog that are not included in the lineup in the table below will be manufactured on a made-to-order basis with a quotation. Please contact us.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q3 | What types of stainless steel sprockets are used? Are there any that can undergo tooth tip hardening treatment? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A3 |
Please refer to the table below for a list of materials used for stainless steel sprockets. The stainless steel sprockets listed in the catalogue are made of austenitic stainless steel (SUS304 series), and due to the characteristics of the material, tooth tip hardening treatment (quenching) cannot be performed. If you require tooth tip hardening treatment using stainless steel, we can manufacture it using martensitic stainless steel (SUS420 series). (Quote required/Made to order) We also offer sprockets that are surface-treated to increase hardness and are recommended for use with high-strength stainless steel chains. (Quotes available, made-to-order products) Please contact us if you have any requests.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q4 | Are there any problems if I use a combination of stainless steel and steel sprockets and chains? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A4 |
We recommend using the same material. Our lineup of stainless steel sprockets is designed to be used in combination with stainless steel chains. For example, using a stainless steel chain in combination with a plated steel sprocket can cause potential corrosion (galvanic corrosion) and lead to early wear. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q5 | The catalogue mentions "tooth hardening treatment," but what kind of treatment is done to the sprockets? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A5 |
The "tooth tip hardening treatment" described in the catalog is a process that hardens the surface by induction hardening. The teeth are hardened to improve their wear resistance and strength. Generally, tooth tip hardening is performed when the rotation speed is high (the number of times the chain engages per unit time is high), when there are few teeth and a small winding angle, or when wear inclusions are present. Generally, carbon steel for mechanical structures is used as the material for tooth tip hardening treatment, but structural alloy steel can also be used upon request. Since it is a type of quenching treatment, it is also called "with teeth hardened treatment = quenching specifications" and "without teeth hardened treatment = unhardened specifications". |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
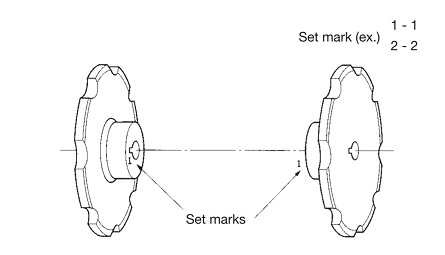
| Q6 | What are the names of each part of a sprocket? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A6 |
The names of each part of the sprocket are as follows: 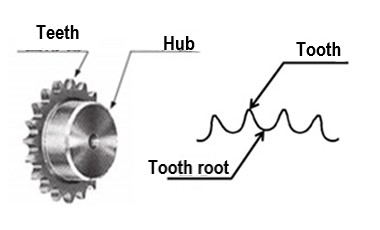


|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q7 | What kind of screw is the "set screw" that comes standard with sprockets? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A7 |
The standard set screw specification for our sprockets is a "hexagon socket set screw (recessed tip)." Standard sprockets other than Fit Bore and special sprockets (estimated or made to order) are not included as a general rule. Stainless steel set screws are included for products with a stainless steel or plated body. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q8 | What are the shapes of sprockets? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A8 |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q9 | I'm thinking of purchasing only the A-type sprocket and welding the hub to it. Will this be a problem? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A9 |
When welding hubs to A-type sprockets, the heat from the welding may make it impossible to maintain quality. Please refrain from welding by yourself and consult with us. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q10 | After placing an order, I found out that the sprocket hub diameter will interfere with the layout. Is it okay to modify the hub? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A10 |
We do not recommend additional work by the customer as this may result in damage or other accidents. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q11 | What does "pilot bore" mean in the catalog? Does this mean that the shaft hole dimensions can be manufactured within the "range of pilot bore to maximum shaft hole diameter" in the catalog? |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A11 |
A pilot bore is a hole that is necessary during the process of manufacturing a sprocket, and are generally not drilled to the tolerances appropriate for shaft assembly. We can manufacture with appropriate tolerances within the range of +1mm or more from pilot bore to the maximum shaft hole diameter. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q12 | What is the maximum size of the sprocket shaft hole that can be machined? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A12 |
The standard pilot bore type shaft hole is machined so that the diameter is less than the "maximum shaft hole diameter" in the dimension table listed for each model number and number of teeth in the catalog. For A-type sprockets that do not have a maximum bore diameter listed, please contact us and we will consider manufacturing them. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q13 | What happens if I use a hub with a hole diameter that exceeds the maximum bore diameter? Are there any problems if the hub is too thin? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A13 |
The hub thickness affects the strength of the sprocket, and if it is insufficient, it may cause cracks or breakage. Consider the conditions under which the chain will be used and design the hub diameter and bore diameter to ensure sufficient strength to prevent damage to the sprocket. We also offer the TOUGH TOOTH sprocket, which is recommended for use with RS-HT chain and increases hub strength without changing the size. Please consider this option if the hub strength is insufficient or if there is not enough space to change the hub size.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q14 | What is the positional relationship between the sprocket teeth and the keyway machining? Can this be specified? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A14 |
Unless otherwise specified, the keyway will be machined in the position shown below.
*If precision is required for the keyway machining position, or if it is to be aligned with a specific tooth position, instructions will be required. When making a request, you will need to provide instructions such as "phase matching" or "parallel use." |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q15 | Is it possible to specify the positional relationship between the sprocket teeth and keyway? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A15 |
It is available as a special form. For "phase alignment," please specify whether the keyway machining position should be aligned to the center of the "tooth tip" or "tooth root." Typically, Tsubaki aligns the center of tooth root for Drive chain and Double pitch, and the tooth tip for Large size conveyor chain. The accuracy of alignment is determined by visual inspection. If you have specific standards, please contact us. *If multiple sprockets are used on the same shaft and particular precision is required, the "parallel use" instruction must be specified. *"Parallel use": See "Q16. When using multiple sprockets on the same shaft, what is the relative positional relationship of the keyways?"Tooth tip alignment 
tooth root alignment 
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q16 | When using multiple sprockets on the same shaft, what is the relative position of the keyways? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A16 |
Generally, this is not taken into consideration. If the relative positional relationship of the keyways needs to be taken into consideration, please specify "parallel use." In that case, please confirm the following two points and provide your instructions. The alignment accuracy is based on visual inspection.
*This is different from "phase matching," which aligns the positional relationship between the keyway and teeth. If phase matching is required, please specify separately. * "Phase alignment": See "Q15. Is it possible to specify the positional relationship between the sprocket teeth and keyway?"Set of 2 (same hub orientation) 
Set of 2 (hub outer-outer) 
Set of 2 (inside hub - inside) 
1 set of 4 pieces (3 pieces in the same direction) 
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q17 | What is Fit Bore? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A17 |
"Fit Bore" means a "sprocket with a completed shaft hole." "Fit" means to fit, and "bore" means to drill a hole. You select the specifications from the service range listed in the catalog, and we will process the shaft hole (shaft hole processing, keyway processing, tap hole processing) and deliver it to you in a state that you can use immediately. We offer "stock items with shaft holes already machined to our specifications" and "made-to-order items where shaft holes are machined to the specifications selected by the customer." You can choose from over 100 million options for shaft hole processing specifications in the TT-net Drawing Library. In addition to sprockets, Fit Bore also offers Belt Sprockets.
Back to Questions
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q18 | Is it possible to deliver sprockets with bearings assembled? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A18 |
We may decline your request depending on the specifications and conditions, but we will consider whether or not it can be manufactured. Please contact us.
Back to Questions
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
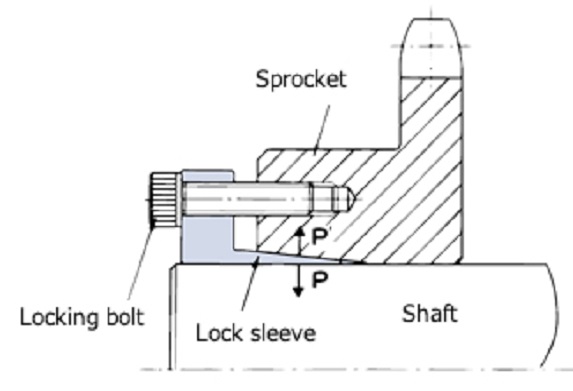
| Q19 | What is Lock Sprocket? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A19 |
Lock Sprocket are friction fastened sprockets that fasten the sprocket to the shaft without using a key, and have the following features:
Always use a torque wrench when tightening the bolts. If the sprocket is not installed correctly with the correct torque, it will slip. Please use shaft diameter tolerance h8 and shaft surface roughness Rq3.2 as the standard. For other precautions, please refer to the catalog and Instruction Manuals and use the product correctly.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q20 | Can you manufacture Lock Sprocket with shaft diameters in inches? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A20 |
Lock Sprocket are not available in inch sizes. Tsubaki Power-Lock are available in inch sizes, so we recommend using Power-Lock. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q21 | Can I use Lock Sprocket on a shaft that has a keyway? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A21 |
It can be used on any shaft with a standard keyway shape. However, please note that the allowable transmission torque will be reduced by approximately 10%. This is because the contact area between the lock sleeve and the shaft is reduced by the size of the key groove. Similarly, when using a Tsubaki Power-Lock, the allowable transmission torque will be reduced. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q22 | Is it okay to use Power-Lock to attach a sprocket to a shaft that has a keyway? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A22 |
Any series other than the EL series can be used as long as the shaft has a standard keyway shape. However, please note that the allowable transmission torque will be reduced by approximately 10%. This is because the contact area between Power-Lock and the shaft is reduced by the size of the key groove. Similarly, the allowable transmission torque will be reduced when Lock Sprocket is used. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q23 | I am considering using Lock Sprocket. Is it possible to apply a surface treatment to Lock Sprocket? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A23 |
Depending on the surface treatment required, we can provide estimates or make to order.
Back to Questions
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q24 | Do you have a stainless steel Lock Sprocket? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A24 |
Stainless steel Lock Sprocket are not available. If you require a stainless steel friction locking type, we recommend combining a Tsubaki RS sprocket (stainless steel specification) with a Tsubaki Power-Lock (stainless steel specification). |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q25 | What kind of surface treatment is possible? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A25 |
Surface treatment involves applying heat treatment or chemical reactions to the surface of a metal to improve not only its appearance but also its corrosion resistance and wear resistance. The three main surface treatments we perform are as follows. (*There are restrictions depending on the size, so please contact us if you have any requests.)
In addition, the "TOUGH TOOTH" sprocket, recommended for use RS-HT chain, is also treated to have a surface hardness of HV800 or higher. Generally, the inner diameter of the shaft hole is not plated.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q26 | I would like to plate my sprockets. What should I pay attention to? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A26 |
We do not recommend that customers perform surface treatments on products after purchase, as this may result in a decrease in strength or other issues.
Back to Questions
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q27 | What kind of sprocket should I choose for Tsubaki's Lube-free Lambda Chain? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A27 |
When selecting two or more strands, please pay attention to transverse pitch size of the chain.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q28 | Can you manufacture sprockets with shear pins? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A28 |
We are unable to determine the specifications for dimensions and breaking strength. If you are unable to provide detailed requirements, unfortunately we will have to decline your order due to quality assurance issues. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q29 | Do your sprockets comply with the RoHS Directive? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A29 |
All of our sprockets comply with the RoHS Directive. If you require a certificate, please request one through the retailer where you purchased the product. *The RoHS Directive is subject to revision. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q30 | If I send a photo of the sprocket, can you identify its specifications? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A30 |
It is not possible to identify an item based on its appearance alone, so specifications cannot be determined from photographs. We are sorry, but we are unable to accommodate your request. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q31 | There is an actual sprocket. Is it possible to send it and make the same one? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A31 |
We can assist you in specifying specifications by requesting a quote. However, even if we check the actual product, we may not be able to determine the specifications. Please note that even if we provide you with a quote, we cannot take responsibility for the specifications. If the item is used, it will no longer retain its original shape, making it difficult to determine the exact dimensions, and if the item is severely damaged, it may not even be possible to determine the general specifications. In some cases, it may not be possible to identify the materials. We ask that you make the final decision on specifications by referring to our opinion. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q32 | What precautions should I take when storing sprockets? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A32 |
Do not store in dusty or dirty places, in places exposed to direct rain, high temperatures, freezing or corrosive atmospheres. Please apply oil with a brush to prevent rust. Please be especially careful with items that are not painted, or even if there is paint, areas such as the shaft holes that are not painted. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q33 | Is grease effective as a sprocket drive lubrication? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A33 |
Applying grease to the meshing area between the sprocket and chain can be effective at low speeds and high loads. However, in dusty places, the dust may be attracted and stuck to the surface, which may accelerate wear. In addition, it is important to oil the spaces between the pins and bushings of the chain to prevent wear and elongation. Grease is sometimes applied to the chain to prevent the oil from flowing out due to external factors (wind, rain, etc.), but conversely, if the grease prevents oil from reaching the spaces between the chain pins and bushings, the oiling effect may be reduced, so please take this into consideration. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q34 | The chain is worn out and I'm planning to replace it with a new one. The sprocket looks good, so I'm wondering if I can still use it. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A34 |
Sprocket wear cannot be determined by its appearance. Just like chains, sprockets also wear, so please inspect and check for any abnormalities such as wear using the inspection methods described in the catalog or Instruction Manuals before making your decision. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q35 | I feel like the sprocket teeth are wearing out quickly. What could be the cause? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A35 |
The table below summarizes possible causes and remedies for wear on a sprocket tooth (root, tooth pressing surface).
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q36 | The side of the sprocket teeth is worn. What could be the cause? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A36 |
The possible causes and solutions are listed in the table below. Also, the inside of the chain link plates may be worn, so please check the chain as well.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q37 | Sometimes the chain rides up onto the sprocket. What could be the cause? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A37 |
The possible causes and solutions are summarized in the table below. If left unattended, this can lead to rapid destruction of the plate (Figure 2), so be sure to inspect and take measures.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q38 | What is Indicator pins? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A38 |
チェッカーズアイは 取替お知らせマークです。 The wear limit of the teeth is marked, and when the wear reaches this mark, it is determined that the limit of service life has been reached. The benefits are as follows:
You can check at a glance when it's time to replace it, which can significantly reduce inspection time and labor costs. Anyone can accurately judge the lifespan, even without skills. From hand inspection to visual inspection. Minimizing contact improves inspection safety. It is installed on theSmart Replaceable Series sprockets for Large size conveyor chain and the large RS sprockets for Drive chain, but can also be installed on other sprockets upon request. Conventional inspection 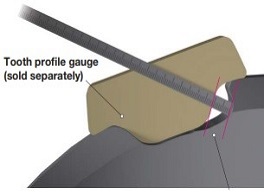
Measure the gap between the worn part and the tooth gauge Indicator pins Inspection You can determine at a glance when it's time to replace the sprocket. 
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q39 | Are there any sprockets that are easy to inspect? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A39 |
We offer sprockets equipped with Indicator pins (replacement notification mark) that lets you know at a glance when it's time to replace them. Standard equipment on Smart Replaceable Series of sprockets (split type, ring replacement tooth type, block replacement tooth type) which require frequent replacement. The standard sprocket equipped with Indicator pins is identified as being painted in "Tsubaki Blue." In addition to being equipped with large size Drive chain sprockets, other conveyor chain sprockets can also be installed upon request. * Indicator pins: See "Q38. What is Indicator pins?"Indicator pins Inspection You can determine at a glance when it's time to replace the sprocket. 
Two locations installed every 180° 
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q40 | Where can I place an order to buy sprockets? How long does it take to deliver? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A40 |
We do not sell directly, so please contact your local distributor or retailer. Please also contact us regarding delivery. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q41 | What are the standards for the tooth profile of Drive chain sprockets? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A41 |
Tsubaki RS sprockets use the JIS standard S tooth profile (also uses the JIS standard U tooth profile in some cases). Other options include BS tooth profiles and special tooth profiles for heavy duty cranked link chain and pin gears. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q42 | Is it necessary to calculate tooth strength when selecting a sprocket? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A42 |
Generally, if working load is less than maximum allowable load of the chain, sprocket tooth will not bend or break, so select it listed in the catalog. However, this needs to be taken into consideration when using heavy-duty chains, so please also check the dedicated sprockets. In calculations, the tension distribution on each tooth in a winding transmission is complex, so calculations are made on one tooth, but in reality, the chain tension is shared by several teeth in a winding transmission, so the chain tension is not borne by just one tooth. Load sharing on teeth 
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q43 | When does "tooth tip hardening treatment" need to be performed on Drive chain sprockets? What is the reason for deciding whether a catalog product has "hardened teeth" or "does not have hardened teeth"? |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A43 |
For Drive chain tooth tip hardening treatment is performed on sprockets that meet the following usage conditions.
Back to Questions
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q44 | Is the lifespan of sprockets the same across all manufacturers? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A44 |
It depends on the manufacturer. The lifespan of a gear is mainly due to wear of the teeth, but our company uses a "tooth tip hardening treatment" that focuses on wear resistance. This is a standard induction hardening, but compared to other companies, the deeper and more uniform heat treatment results in less tooth wear over long periods of use. "Hardening" is a strength of Tsubaki products. Please consider Tsubaki sprockets, which have superior wear resistance.
Cross-section comparison of tooth tip hardening treatment (discolored area of tooth tip is hardened layer)
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q45 | What is the usable temperature range of the sprocket? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A45 |
The appropriate operating temperature range for RS sprockets is -10°C to 150°C, while the appropriate operating temperature range for stainless steel RS sprockets is -20°C to 400°C. Not only do temperature-related changes in strength have to be considered, but also the limitations of chain lubrication. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q46 | Can I use a general standard RS sprocket in an environment where a cold-resistant Drive chain is used (below -10°C)? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A46 |
The standard sprockets listed in the catalog are made of carbon steel or rolled steel for machine structures, and are not recommended for use in temperatures below -10°C as their strength will decrease. We may be able to propose countermeasures such as special sprockets made to order using different materials. Please contact us regarding products with operating temperature ranges not listed in the catalog. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q47 | Can I use a standard RS sprocket with Heavy duty drive chain? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A47 |
Standard sprockets with hardened teeth can be used, but there are many cases where the key surface pressure is insufficient. We offer "TOUGH TOOTH" as a recommended sprocket for Heavy duty drive chain, so please consider it. The stronger the chain, the more important it is to check the key pressure, etc. Although it is possible to increase the surface pressure by using a double key or lengthening the hub, we recommend the "TOUGH TOOTH" with its stronger hub from the standpoint of space saving and price. Also, when using H-class chains such as HT Heavy Duty chains and Super-H chains in multiple strands, standard RS sprockets cannot be used because the transverse pitch of the teeth is different. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q48 | Can standard RS sprockets be used with BS standard chain? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A48 |
Cannot be used with JIS standard RS sprockets as the three basic dimensions (pitch, roller diameter, and roller link inner width) are different. For BS standard chains, we offer BS/DIN standard dedicated sprockets. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q49 | Can I use a standard RS sprocket for the pin gear? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A49 |
A special sprocket with a special tooth profile is required. Standard RS sprockets cannot be used as the meshing with the chain is different from that of a winding transmission. To make an object move linearly or in a rotational direction, roller chains and gears are generally used, passing through a reducer from a drive source (such as a motor). Winding transmission using roller chains requires a large space, and gears require precision machining, which leads to problems such as high costs. In such cases, a pin gear drive is ideal. As shown in Figure 1, pin gear drive uses a chain with a pin gear attachment wound around the outer periphery of a drum or table instead of a wheel, and a sprocket with a special tooth profile (pin gear sprocket) instead of a pinion gear. For linear motion, a chain with a pin gear attachment is installed in a straight line instead of a rack, as shown in Figure 2. "Pin Gear Drive Unit" that includes a pin gear and a wheel or rack is also on sale. 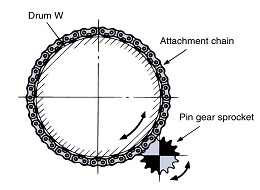
[Figure 1] 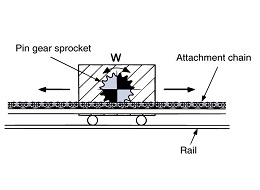
[Figure 2] |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q50 | Can you manufacture chain tensioners? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A50 |
We offer standardized tensioners and idlers. Please consider our specifications. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
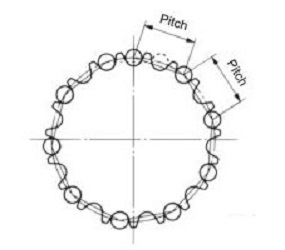
| Q51 | What causes uneven sprocket rotation and how can you fix it? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A51 |
One of the causes of uneven rotation is fluctuations in the chain speed. The chain meshes with the sprockets in a polygonal pattern. Therefore, as shown in the diagram below, the height of engagement (radius from the center of the sprocket) differs when the gears engage at the tangent position of the circle and when they engage at the string position. As a result, even if the drive sprocket rotates at a constant speed, the chain's speed will vary by the radius ratio. The speed fluctuation rate can be calculated using the following formula. Speed fluctuation rate = (V2-V1)/V2=1-cos(180°/Z) (Z is the number of teeth) Increasing the number of teeth results in smoother rotation and power transmission. We generally recommend 15 teeth or more. V2 Chain Speed Max V1 Chain Speed Min 
<Rotation irregularities> Chain speed fluctuations and the properties of the sprocket cause uneven rotation of the driven sprocket. Furthermore, there are also influences from eccentric mounting errors of the sprocket and manufacturing errors of the chain and sprocket. Increasing the number of teeth on the drive sprocket (larger diameter) will result in smoother transmission and less rotational irregularities. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q52 | Drive chain is vibrating. Could the sprocket be the cause? Is there anything I can do about it? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A52 |
The sprocket may also be the cause. The causes and solutions are as follows: polygon movement When chordal action (polygonal movement of the sprocket and chain) is involved, polygonal movement can be suppressed by selecting as many teeth as possible. Generally, 15 or more teeth are recommended. * "Cordal Action": See "Q51. What are the causes and solutions for uneven sprocket rotation?" |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q53 | What are the appropriate speed ratios and winding angles for RS sprockets for Drive chain? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A53 |
The speed ratio for roller chain transmission is normally up to 7:1. At very low speeds, it is possible to go up to about 10:1.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
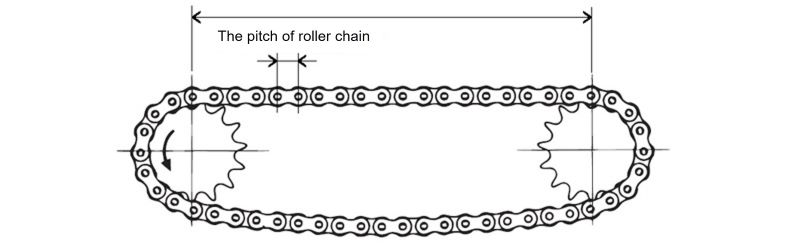
| Q54 | What is the appropriate sprocket center distance for RS sprockets for Drive chain? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A54 |
The shortest distance is sufficient as long as the teeth of the two sprockets do not come into contact. The most desirable center distance between the two shafts is about 30 to 50 times the pitch of the roller chain being used. However, when fluctuating loads are applied, it is appropriate to keep it 20 times or less. Approximately 30 to 50 times the pitch of the roller chain
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
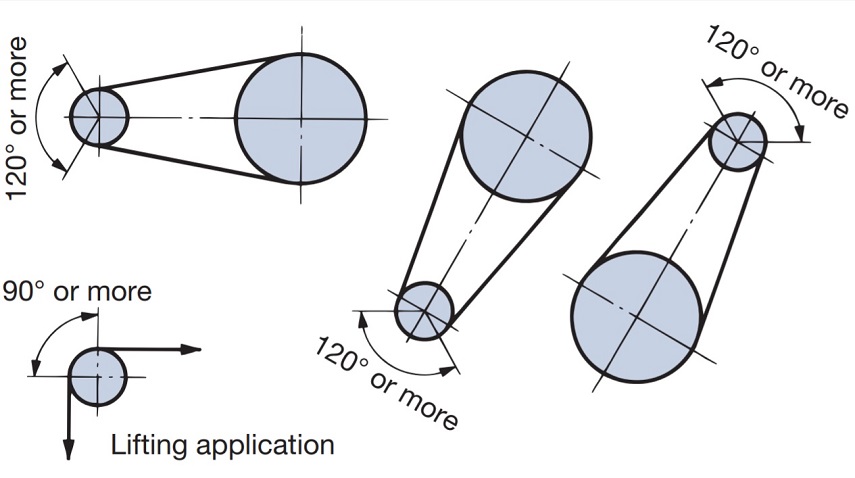
| Q55 | Are there any rules for the layout of RS sprockets for Drive chain? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A55 |
A typical roller chain transmission arrangement is as follows:
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
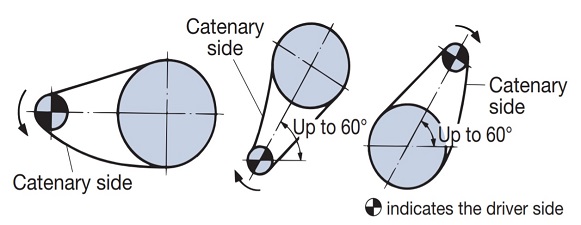
| Q56 | Are there any layouts or positions that require special attention when using RS sprockets for Drive chain? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A56 |
In the following cases, care must be taken with the layout and placement. We recommend using idlers and tensioners.

Figure 1) Layout for short center distance 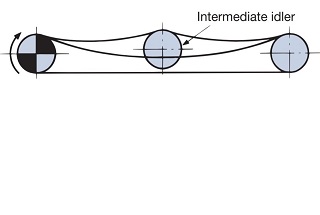
Figure 2) Layout for long center distance 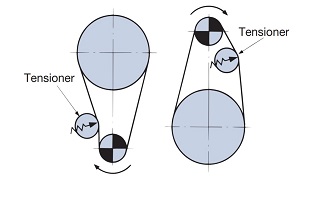
Figure 3) Vertical transmission |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
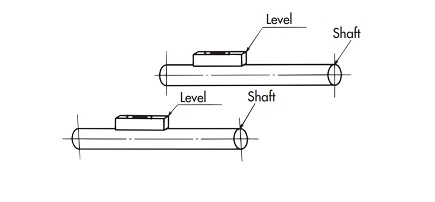
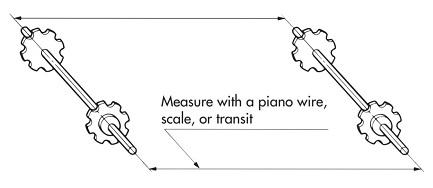
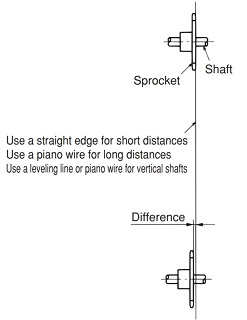
| Q57 | What is the installation accuracy and installation procedure for RS sprockets for Drive chain? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A57 |
When installing, please pay attention to levelness and parallelism and follow the instructions below to install correctly.
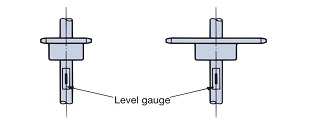
Figure 1) Shaft horizontality 
Figure 2) Parallelism of shafts 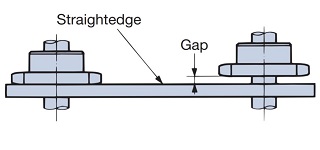
Figure 3) Misaligned sprockets |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
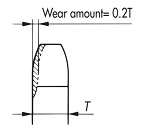
| Q58 | What happens to the RS sprockets for Drive chain when they reach the end of their life? What are the key points to check? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A58 |
Check the wear of the teeth to determine the end of life and when it is time to replace the sprocket. Worn teeth reduce the strength of the sprocket, which can have a negative effect on chain transmission. By inspecting the sprocket regularly, you can replace it with a new one before any problems occur. Check the following points:
To reduce inspection man-hours and improve safety, we can manufacture sprockets equipped with Indicator pins that indicate when it is time to replace them. Tooth Thickness Usage Limit/B Dimension Table
When rotating forward or reverse When rotating in one direction Tooth thickness usage limit/B dimension (figure) 
Figure 2) The side of the tooth is being worn down |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q59 | What are the symptoms of improper installation of RS sprockets for Drive chain and what should I check? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A59 |
[Symptoms] If you experience any of the following symptoms, please check the sprocket and its installation again.
[Inspection points] The cause can be determined by checking the sprocket meshing. If it is not normal, re-inspect and correct it.
The cause of the abnormality may be improper installation of the sprocket or a twisted roller chain. If any abnormality is found, replace the sprocket with a new one, as using the sprocket as is will have a negative effect on the roller chain transmission. 
Figure 1) Sprocket tooth contact 
Figure 2) The side of the tooth is being worn down |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q60 | Can RS sprocket for drive chain be used for Double Pitch S roller Chain? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A60 |
Double pitch S rollers cannot be used with RS sprockets with 29 or fewer teeth; Double pitch sprockets are required. Standard RS sprockets for Drive chain with 30 or more teeth. (This is because the pitch circle diameter (PCD) is an approximate value for sprockets with 30 or more teeth.) Additionally, sizes larger than RF2060 cannot be used in multiple strand because transverse pitch is different. In this case, it is considered a special-shaped chain, so we will consider manufacturing a special-shaped sprocket based on the chain diagram. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q61 | Can RS sprockets for Drive chain be used with Small size conveyor chain? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A61 |
RS sprockets for Drive chain can be used with RS type small conveyor attachment chains. However, please note that if the sprocket diameter is small or the attachment is special, you will need to consider interference with the sprocket. For Double pitch, use Double pitch sprockets. However, if Double pitch S rollers are used and the number of teeth is 30 or more, RS sprockets can be used. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q62 | Why is an odd number of teeth recommended for Double pitch sprockets designed specifically for Double pitch (S roller) ? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A62 |
For S rollers, an odd actual number of teeth is recommended as this will increase wear life. In Double pitch sprockets, the number of teeth that actually mesh is called effective number of teeth, and the number of apparent teeth is called actual number of teeth.If the chain is an S-roller type, the chain will engage every other tooth (Fig. 1). When actual number of teeth for an S roller is odd (see Figure 3), the rollers on the first rotation will mesh with numbers 1 to 10, skipping every other tooth, but from the second rotation onwards they will start meshing with number 11, a different tooth from the previous rotation. Because the rollers mesh with different teeth on each rotation of the sprocket, there is less wear and the rollers have a longer lifespan. In the case of R rollers, each tooth engages (Fig. 2). |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q63 | I'm using Hollow Pin Double pitch. What kind of sprockets can I use? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A63 |
As with standard RF Double pitch, RS sprockets for Drive chain can be used when the number of teeth is 30 or more. It cannot be used with 29 teeth or less, so Double pitch sprocket is required. For multiple strand, sizes RF2060 and above cannot be used due to the different transverse pitch. In this case, it is considered a special-shaped chain, so we will consider manufacturing a special sprocket based on the chain diagram. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q64 | What is the installation accuracy and installation procedure for Small size conveyor chain? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A64 |
When installing, please pay attention to levelness and parallelism and follow the instructions below to install correctly.
Figure 1 Measuring the horizontality of the shaft Figure 2: Measuring the parallelism of the shaft |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q65 | What is the end of life for Double pitch sprockets for Small size conveyor chain? What are the key points to inspect? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A65 |
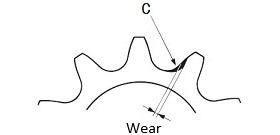
Figure 2: Sprocket tooth wear 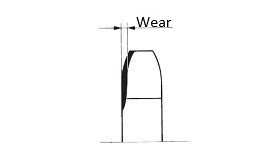
Fig. 3 Sprocket tooth wear (side) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q66 | What is the minimum number of teeth on a sprocket for Large size conveyor chain? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A66 |
Considering the chain grip, a minimum of 6 teeth is required. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q67 | Regarding sprockets for Large size conveyor chain, is it possible to manufacture A-type sprockets without hubs? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A67 |
Yes, but it is a made-to-order product, so please provide us with a quote. If the part is intended to be welded, this may lead to defects depending on the material. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q68 | Do Large size conveyor chain sprockets have hanging holes? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A68 |
For products with hanging holes, please check the catalog. For sprockets with hanging holes, the hanging hole dimensions and number of holes are specified in the hanging hole dimension list in addition to the sprocket body dimension table. Sprockets with model numbers and tooth counts not listed do not have hanging holes. If you have any requests, we will consider production and provide a quote on a case-by-case basis, so please let us know the specific location, size, and number. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q69 | What is the installation accuracy and installation procedure for Large size conveyor chain sprockets? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A69 |
When installing, please pay attention to levelness and parallelism and follow the instructions below to install correctly.
*Installation accuracy is a general value from the perspective of the conveyor chain itself. If there are limitations on the accuracy of the conveyor itself, please comply with those limitations. Figure 1 Measuring the horizontality of the shaft Figure 2: Measuring the parallelism of the shaft |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
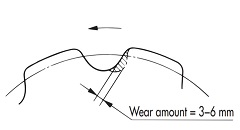
| Q70 | When does Large size conveyor chain sprocket reach the end of its life? What are the key inspection points? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A70 |
Use Figure 1 as a guide for the wear limit of the sprocket tooth surface. Depending on the size, the lifespan is 3 to 6 mm. If the chain engages with a sprocket with worn teeth, it will have adverse effects such as premature chain wear. If the teeth are worn, replace the sprocket. If the side of the sprocket teeth is worn, refer to Table 1 and take appropriate measures to address the cause. We can manufacture sprockets equipped with Indicator pins that indicates when the sprocket needs to be replaced, reducing inspection time and improving safety.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||