technical data Top chain Selection
If you would like to see the selection procedures and important points, please proceed below.
If you would like to narrow down or tentatively select a product series,
Please click here.
If your usage conditions have been decided and you would like a detailed selection,
Please click here.
Selection of Plastic Roller table
Follow the steps below to select Plastic Roller table and rails that are best suited to your transport conditions.
- 1. Check the transport conditions
- 2. Chain type selection
- 3. Chain size selection
- 4. Calculation of required power
Step 1. Check the transport conditions
Check the transport conditions.
Transportation condition confirmation items
| 1.Transported items | (1)Material |
|---|---|
| (2) Mass per piece (g/piece) | |
| (3) Dimensions (length x width) mm | |
| 2.Transportation route | (1) Transport layout |
| (2) Conveyor length m | |
| (3) Space m | |
| 3.Transportation conditions | (1) Conveyance amount /min |
| (2) Transfer interval mm | |
| (3) Conveyor speed m/min | |
| 4.Usage environment | (1) Temperature ℃ |
| (2) Corrosive conditions such as chemicals, water, and humidity (see Corrosion resistance to various liquids) (if applicable, name of liquid) |
2-(4) Transport layout and other notes
Step 2. Select the chain type
ST type...Used when the transported item needs to be transferred horizontally (horizontal loading or unloading).
RT type: Used when there is no lateral transfer of transported items (direct loading/direct unloading). (However, lateral transfer is possible if the transported items are large items such as pallets or cases.)
Step 3. Determine the chain size
Select the chain size for Plastic Roller table based on Table 1. Selection table by transported item and Table 2. Transport capacity table for ST and RT types of Plastic Roller tables.
Note) For information on wearstrip, please refer to wearstrip section.
Table 1. Selection table based on transported item dimensions
| Chain size | Transported object dimensions (mm) |
|---|---|
| 300 Series | 30 or more |
| 400 Series | 44 or more |
| 500 Series | 55 and over |
| 600 Series | 66 or more |
Note: The dimensions of the transported item refer to the bottom dimensions of the item. Please note that the dimensions of the transported item will vary depending on the balance between the bottom dimension and height, so please use this as a guide only.
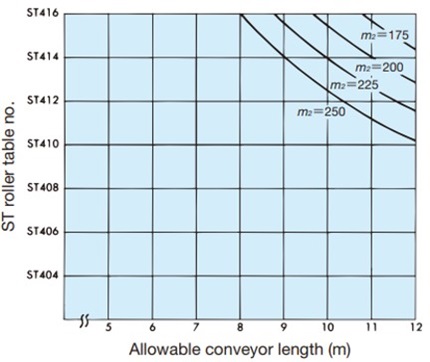
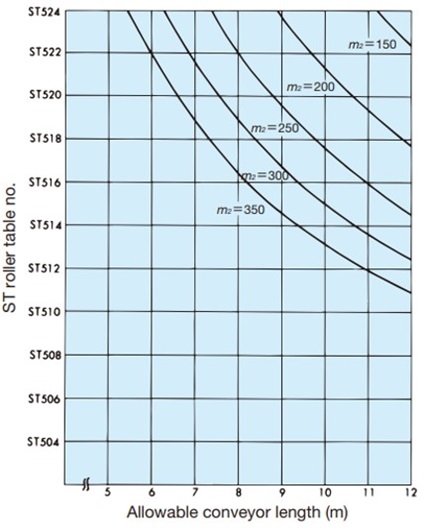
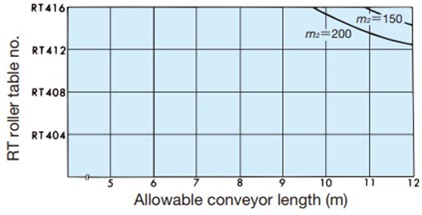
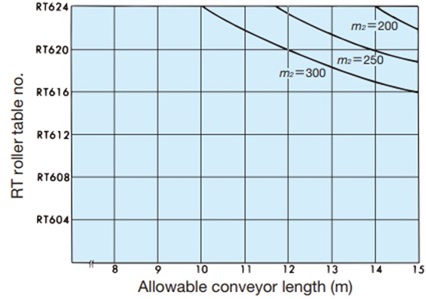
Table 2. Conveying capacity of the ST and RT types of Plastic Roller tables
| How to read the table: ST type | How to read the table: RT type | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
m 2 = 300kg/m 2When conveyor length is 10m, ST504 to ST514 m 2 = Load mass (kg/m 2) = Weight of transported object (kg) Base area of transported object (m 2) ST300
ST400
ST500
|
m 2 = 300kg/m 2When conveyor length is 10m, ST504 to ST514 m 2 = Load mass (kg/m 2) = Weight of transported object (kg) Base area of transported object (m 2) RT300
RT400
RT500
RT600
|
・How to calculate the load mass m2 (kg/m 2) (for round objects)
m2 = Load mass (kg/m 2) = Weight of transported object (kg) Base area of transported object (m 2)
m2 = ω × 106 D2sin60° (kg/m2)
- m2: Loading mass (kg/m 2)
- ω: Mass of one transported item (kg)
- D: Outer diameter of the transported item (mm)
Example: 350ml can (outer diameter Φ66, 0.37kg/can)
m2 = 0.37 × 106 662 × sin60° = 98kg/m2

Step 4. Calculate the required power
The required power is calculated using the following formula:
kW = X・(m1 + m2・H)・S・v 5565・η
- kW = required power
- m1 = Approximate chain mass (kg/m)
- m2 = loading mass (kg/m 2)
- H = Conveying width [effective width] (m)
- S = center distance (m)
v = chain speed (m/min)
ηNote) = Mechanical transmission efficiency of the drive unit
X = coefficient of lubrication (not to be confused with coefficient of friction)
- ・When the chain body is lubricated, X = 0.3
- ・Without chain body lubrication: X = 0.4
Note: Please check the drive unit used to determine transmission mechanical efficiency.