technical data Drive chain Roller Chain Selection
10. Chain type pin gear drive selection method Note: What is a chain type pin gear?
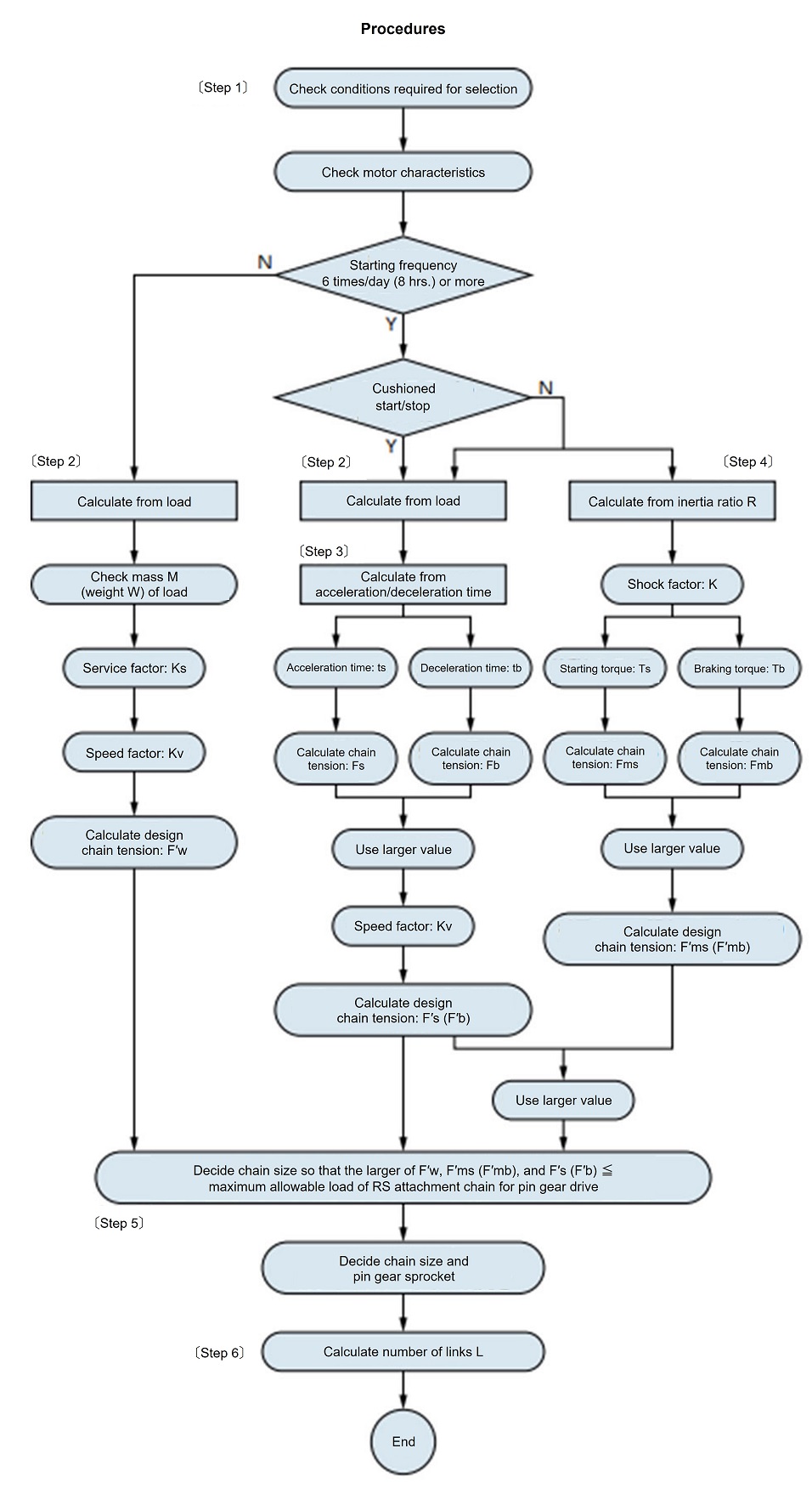
1. Speed Considerations
This selection method is applicable when the relative chain speed is 50 m/min or less.
(Example of action when speed is below 50m/min)
- If you are considering a linear application:
Change to a winding method such as roll drive - If you are considering a wrapping application:
Chain mounting diameter reduced
| Relative Chain Speed m/min |
Pin gear Speed Factor |
|---|---|
| Under 15 | 1.0 |
| 15以上30未満 | 1.2 |
| 30以上50未満 | 1.4 |
2. Sprocket Considerations
Please use a chain-type pin gear sprocket with 13 or more teeth.
18 teeth recommended.
3. Example of chain-type pin gear drive
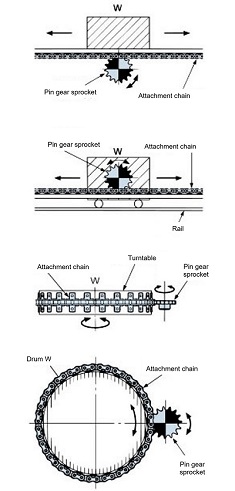
Please also refer to the formulas (here), coefficients (here) used for chain selection, and how to calculate the moment of inertia (here).
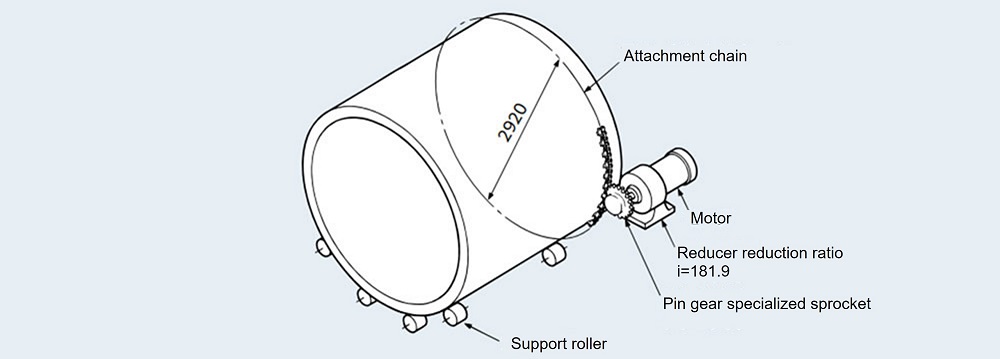
Chain type pin gear drive selection example
| SI units |
|---|
Step 1: Check the machine and motor characteristics
Step 2 Calculate from the loadRotational speed of pin gear driving sprocket n = 1750 ×
1
181.9
Relative chain speed V =
220 × π × 9.6
1000
= 6.6 (m/min) Assume some impact due to cutting machine Since the mass of the load is unknown, the applied tension is calculated from the drive torque. Motor rated torque Pin gear drive sprocket shaft torque Chain tension F = 2T d 1000 = 2 × 1.49 220 1000 = 13.6 (kN) Corrected chain tension F'w = F × Ks × Kv = 13.6 × 1.3 × 1.0 Step 3: Calculate from acceleration/deceleration timeActing torque Tm =
Ts + Tb
2 × 100
× Tn =
290 + 305
2 × 100
× 0.00819 Since the load is unknown, the motor rated torque Tn = T ℓ is used, Acceleration time ts =
(Im + I ℓ) × n 1
9550 × (Tm - T ℓ)
=
(0.00425 + 0.00072) × 1750
9550 × (0.0244 - 0.00819)
Motor brake torque Tb = 0.00819 × 1.8 = 0.0147 (kN・m) Deceleration time tb =
(Im + I ℓ) × n 1
9550 × (Tb + T ℓ)
Moment of inertia of the motor shaft converted load II ℓ = 0.00072 (kg・m 2) Fw = F= 13.6 (kN) [value obtained in step 2] Since tb < ts, find the chain tension during deceleration. Angular velocity of the motor shaft ω = 2 π × n 1 = 2 π × 1750 = 11000 (rad) Motor shaft angular deceleration ωb =
ω
60 × tb
=
11000
60 × 0.040
Chain tension during deceleration Fb =
I ℓ × ωb × i
1000 ×
d
(2 × 1000)
+ Fw Corrected chain tension during deceleration F'b = Fb × Kv = 19.1 × 1.0 Step 4 Calculate from inertia ratio RInertia ratio R = I ℓ Im = 0.00072 0.00425 = 0.17 From Table 4, impact coefficient K = 0.23 Chain tension at start Fms =
Ts × i
d
2 × 1000
× 100
× Tn Chain tension during braking Fmb =
Tb × i
d
2 × 1000
× 100
× Tn × 1.2 From Fms > Fmb Step 5 Compare (1)(2)(3)Compare (1), (2), and (3) and select a chain with pin gear attachments that has Maximum allowable load that satisfies the maximum applied tension (2) of 19.1 kN. Maximum allowable load when using RS120 attachment chain with pin gear The pitch diameter of the pin gear sprocket is Φ220, so the sprocket has 18 teeth. Recalculate steps 2, 3 and 4. [Step 2] F = 2T d 1000 = 2 × 1.49 222.49 1000 = 13.4 (kN) F'w = F × Ks × Kv = 13.4 × 1.3 × 1.0 = 17.4 (kN) [Step 3] Fb =
Iℓ × ωb × i
1000 ×
d
(2 × 1000)
+ Fw Corrective chain tension during deceleration F'b = Fb × Kv = 18.8 × 1.0 = 18.8 (kN) [Step 4] Fms =
Ts × i
d
2 × 1000
× 100
× Tn Correction chain tension F'ms = Fms × K × Kv = 38.8 × 0.23 × 1.0 = 8.92 (kN) Since both corrected chain tensions are within Maximum allowable load, chains with pin gear attachments and sprockets for pin gears can be used. [Step 6] Calculate the number of links L Calculating the number of links L Equivalent to 242 link standard length (38.1 x 242 = 9220.2 mm) |
| {gravity unit} |
|---|
Step 1: Check the machine and motor characteristics
Step 2 Calculate from the loadRotational speed of pin gear driving sprocket n = 1750 ×
1
181.9
Relative chain speed V =
220 × π × 9.6
1000
= 6.6 (m/min) Assume some impact due to cutting machine Since the mass of the load is unknown, the applied tension is calculated from the drive torque. Motor rated torque Pin gear drive sprocket shaft torque Chain tension F = 2T d 1000 = 2 × 152 220 1000 = 1380 (kgf) Corrected chain tension F'w = F × Ks × Kv = 1380 × 1.3 × 1.0 Step 3: Calculate from acceleration/deceleration timeActing torque Tm =
Ts + Tb
2 × 100
× Tn =
290 + 305
2 × 100
× 0.835 Since the load is unknown, the motor rated torque Tn = T ℓ is used, Acceleration time ts =
(GD 2 m + GD 2ℓ) × n 1
375 × (Tm - t ℓ)
=
(0.017 + 0.00288) × 1750
375 × (2.48 - 0.835)
Motor brake torque Tb = 0.835 × 1.8 = 1.50 (kgf・m) Deceleration time tb =
(GD 2 m + GD 2ℓ) × n 1
375 × (Tb + T ℓ)
Motor shaft converted load GD 2 GD 2ℓ = 0.00288 (kgf・m 2) Fw = F = 1380 (kgf) [value obtained in step 2] Since tb < ts, find the chain tension during deceleration. Angular velocity of the motor shaft ω = 2 π × n 1 = 2 π × 1750 = 11000 (rad) Motor shaft angular deceleration ωb =
ω
60 × tb
=
11000
60 × 0.040
Chain tension during deceleration Fb =
GD 2ℓ / 4 × ωb × i
d
(2 × 1000)
× G
+ Fw Corrected chain tension during deceleration F'b = Fb × Kv = 1940 × 1.0 Step 4 Calculate from inertia ratio RInertia ratio R = GD 2ℓ GD 2 m = 0.00288 0.017 = 0.17 From Table 4, impact coefficient K = 0.23 Chain tension at start Fms =
Ts × i
d
2 × 1000
× 100
× Tn Chain tension during braking Fmb =
Tb × i
d
2 × 1000
× 100
× Tn × 1.2 From Fms > Fmb Step 5 Compare (1)(2)(3)Compare (1), (2), and (3) and select a chain with pin gear attachments that has Maximum allowable load that satisfies the maximum applied tension (2) of 1940 kgf. Maximum allowable load when using RS120 attachment chain with pin gear The pitch diameter of the pin gear sprocket is Φ220, so the sprocket has 18 teeth. Recalculate steps 2, 3 and 4. [Step 2] F = 2T d 1000 = 2 × 152 222.49 1000 = 1370 (kgf) F'w = F × Ks × Kv = 1370 × 1.3 × 1.0 = 1780 (kgf) [Step 3] Fb =
GD2ℓ/4 × ωb × i
d
(2 × 1000)
× G
+ Fw Corrective chain tension during deceleration F'b = Fb × Kv = 1930 × 1.0 = 1930 (kgf) [Step 4] Fms =
Ts × i
d
2 × 1000
× 100
× Tn Correction chain tension F'ms = Fms × K × Kv = 3960 × 0.23 × 1.0 = 911 (kgf) Since both corrected chain tensions are within Maximum allowable load, chains with pin gear attachments and sprockets for pin gears can be used. [Step 6] Calculate the number of links L Calculating the number of links L Equivalent to 242 link standard length (38.1 x 242 = 9220.2 mm) |

