technical data Reducer Small Gear Motor Handling
This section describes general handling of Gear Motor, Hypoid Motor, and Croise Motor.
For details, please refer to Instruction Manuals attached to the product.
Installation
1. Installation direction
- ・ Gear Motor, Hypoid Motor, mini series
There are no restrictions on the installation direction. It can be installed horizontally, vertically, or at an angle.
- -Croise Motor
- CSMA/CSMR series
There are no restrictions on the installation direction for reducer frame numbers 13 to 28. They can be installed in any direction, horizontally, vertically, or at an angle.
Horizontal installation is standard for reducer frame sizes 32 to 50. If you require a different installation direction, please specify this when ordering. - HCMA/HCMR series
Horizontal installation is standard. If you require a different installation direction, please specify this when ordering.
- CSMA/CSMR series
Installation
1. Foot mount type
- - Use a strong, flat mounting base that is less susceptible to vibrations during operation, and after removing any dirt or foreign matter from the mounting surface, secure it firmly with four bolts.
- - When connecting with a coupling, be sure to center the shaft properly. Eccentricity of the shaft will shorten the life of the bearings, gears, and shaft, and will also cause noise and vibration.
- - Center the chain or belt accurately and adjust the tension so that the load on the output shaft does not exceed the specified value.
- - When connecting, please be careful not to hit the output shaft, coupling, pulley, or sprocket too hard, as this may damage the output shaft bearing.
2. Flange mounting type
- - For flange mounting, use a strong, flat flange that is less susceptible to vibrations during operation, and after removing any dust or foreign matter from the installation surface, secure it firmly with four bolts.
- - When connecting with a coupling, be sure to center the shaft properly. Eccentricity of the shaft will shorten the life of the bearings, gears, and shaft, and will also cause noise and vibration.
- - Center the chain or belt accurately and adjust the tension so that the load on the output shaft does not exceed the specified value.
- - When connecting, please be careful not to hit the output shaft, coupling, pulley, or sprocket too hard, as this may damage the output shaft bearing.
3. Face mount type
- - When installing on the machine body, please use the taps on the case.
- - When connecting with a coupling, be sure to center the shaft properly. Eccentricity of the shaft will shorten the life of the bearings, gears, and shaft, and will also cause noise and vibration.
- - Center the chain or belt accurately and adjust the tension so that the load on the output shaft does not exceed the specified value.
- - When connecting, please be careful not to hit the output shaft, coupling, pulley, or sprocket too hard, as this may damage the output shaft bearing.
4. Hollow shaft type
4-1. Mounting to the driven shaft
- The hollow shaft inner diameter tolerance is manufactured to JIS H8. The driven shaft should normally be finished to h7, but in cases of large impacts or radial loads, use a slightly tighter fit of around js6 or k6.
- - When installing onto the driven shaft, apply molybdenum disulfide grease to the surface of the driven shaft and the inner diameter of the hollow output shaft before inserting.
- - If you make and use a jig like the one shown on the right, you can insert it smoothly.
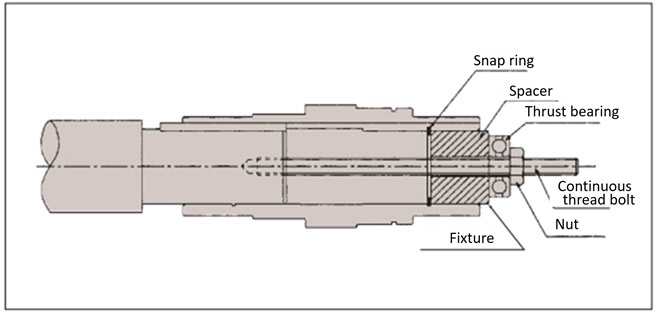
4-2. Fixing to the driven shaft
A. When there is a step on the driven shaft
Fabricate an end plate as shown in the diagram below and secure the hollow output shaft and driven shaft in place.
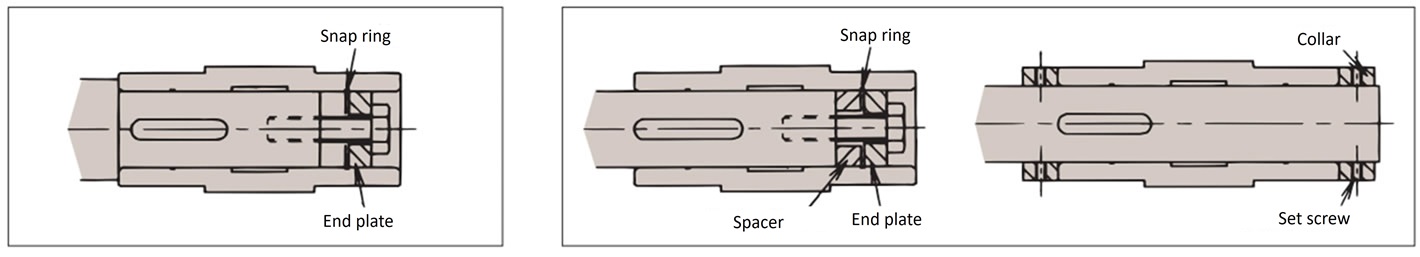
B. Example when there is no step on the driven shaft
There are two fixing methods:
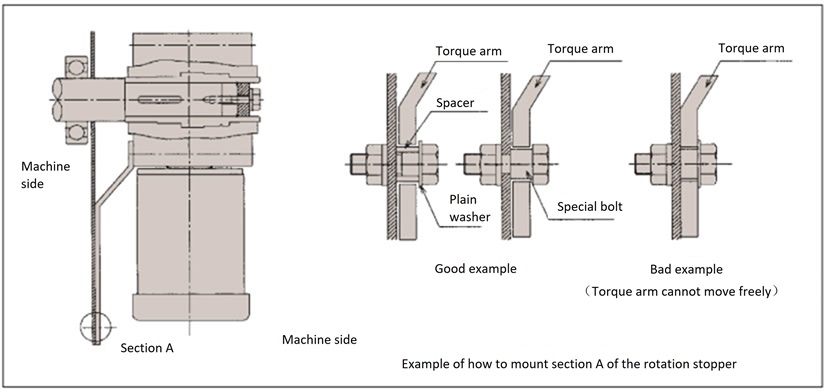
4-3. Torque arm rotation stopper
・Attach the torque arm to the driven machine side of Hypoid Motor using a hexagon socket head bolt.
The torque arm's anti-rotation section must have some degree of freedom between Hypoid Motor and the driven shaft, and the torque arm must never be secured with an anti-rotation bolt. A lack of freedom can cause damage to the bearings inside the reducer.
If the start-up frequency is high or if the motor is repeatedly rotated forward and backward, installing a rubber bushing between the torque arm and the anti-rotation bolt (or spacer) will reduce the impact.
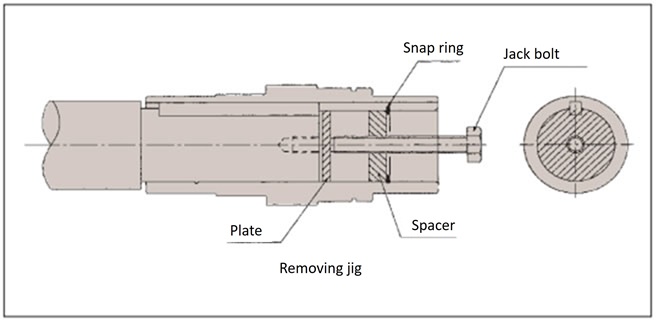
4-4. Removal from the driven shaft
- - Remove the driven shaft from the hollow output shaft so that no excess force is applied between the casing and the hollow output shaft.
- - If you make and use a jig like the one shown on the right, removal will be smooth.
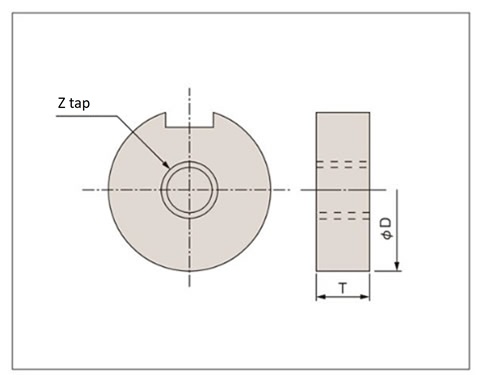
Recommended plate dimensions (HMMT, HMTA, HMTR, Kroese)
| Eligible products (Representative frame number) |
Output hollow shaft hole diameter | Plate | Stop Ring Size | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ΦD | T | Z | |||
| HMMT40 | Φ18 | 17.5 | 8 | M8 | C18 |
| HMTA-20 frame | Φ20 | 19.5 | 6 | M8 | C20 |
| HMMT60・90 | Φ22 | 21.5 | 8 | M8 | C22 |
| CSMA-16 frame | Φ25 | 24.5 | 9 | M10 | C25 |
| HMTA-30 frame CSMA-22 slot |
Φ30 | 29.5 | 9 | M12 | C30 |
| HMTA-35 frame | Φ35 | 34.5 | 12 | M12 | C35 |
| CSMA-28 slot | Φ40 | 39.6 | 12 | M12 | C40 |
| HMTA-45 frame | Φ45 | 44.5 | 15 | M16 | C45 |
| CSMA-32 frame | Φ50 | 49.5 | 12 | M16 | C50 |
| HMTA-55 frame | Φ55 | 54.5 | 18 | M18 | C55 |
| CSMA-40 frame | Φ70 | 69.5 | 14 | M24 | C70 |