technical data Drive chain Roller Chain Selection
11. How to calculate the moment of inertia
Rotating body
| Shape | overview | I (moment of inertia) calculation method (SI units) |
{GD 2 Calculation Gravitational Unit} |
|---|---|---|---|
| Right circular cylinder |

|
I = 1 2 Mr2 (kg・m2) | GD2 = 1 2 WD2 (kgf・m2) |
| Hollow right circular cylinder |

|
I = 1 2 M(r12+r22) (kg・m2) |
GD2 =
1
2
W(D12 + D22) (kgf・m2) |
| SI units | {gravity unit} | |
|---|---|---|
| Moment of inertia (I) and flywheel effect (GD 2) | 1kg・m2(I) | 4kgf・m2(GD2) |
linear moving body
| Drive type | overview | I (moment of inertia) calculation method (SI units) |
{GD 2 Calculation Gravitational Unit} |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chain |
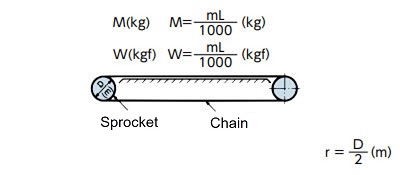
|
I = Mr2(kg・m2) | GD2 = WD2(kgf・m2) |
| Cart drive |
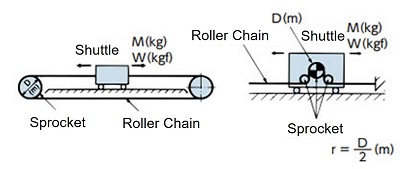
|
I = Mr2(kg・m2) | GD2 = WD2(kgf・m2) |
| Pin gear drive |
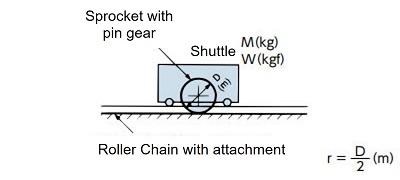
|
I = Mr2(kg・m2) | GD2 = WD2(kgf・m2) |
| Hanging transmission |
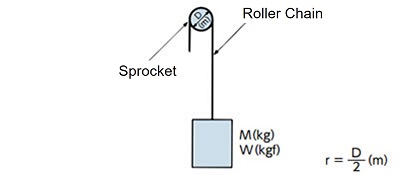
|
I = Mr2(kg・m2) | GD2 = WD2(kgf・m2) |
|
When converting the load moment of inertia to the motor shaft
|
Load moment of inertia I Iℓ = n2n12I = I i 2 (kg·m 2) I ℓ = M V 2 π n 1 2 (kg・m 2) |
Load moment of inertia GD 2 GD 2ℓ = n 2 n 1 2 GD 2 = GD 2 i 2 (kgf·m 2) GD 2ℓ = W V π n 1 2 (kgf・m 2) |
|
Note: The above does not include the mass of the sprocket and chain.

