technical data Reducer DCBL Hypoid Motor Handling
This section describes general handling of DCBL Hypoid Motor drivers.
For details, please refer to Instruction Manuals attached to the product.
Torque arm design
When using a standard torque arm or designing and manufacturing your own torque arm, please check the strength of each element as follows:
1. Check the torque arm and fixing bolts
Check using torque arm reaction force R.
R = T + W × G C
2. Bearing selection
Check bearing reaction forces A and B.
A (bearing a) = L1 × (R - W) -D × R L2
B(bearing b) = (L1 + L2) × (R - W) - D × R L2
*The output torque is + when rotating in the direction shown on the left, and - when rotating in the opposite direction.
- T: Output torque N・m{kgf・m}
- W: Weight of reducer kg{kgf}
- R: Torque arm reaction force kg {kgf}
- G: Distance between the center of the driven shaft and the center of gravity of the reducer m
- C: Distance between the driven shaft center and the anti-rotation stopper m
- D: Distance between the center of the reducer and the anti-rotation stopper m
- L1: Distance m between the center of the reducer and bearing b
- L2: Distance between bearing a and bearing b m
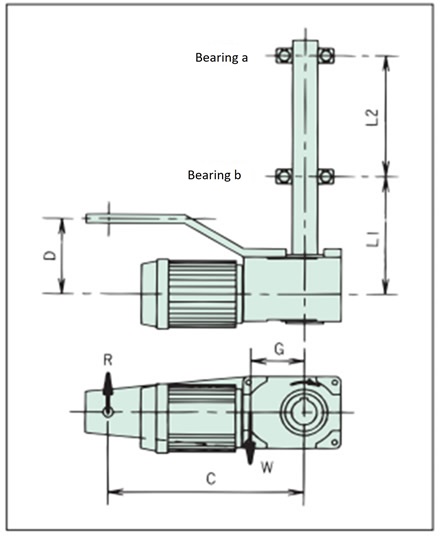
Dimensions when using optional torque arm (approximate values)
| Model number | DCHM020-20H10~60 | DCHM040-30H10~50 | DCHM075-35H10~50 |
|---|---|---|---|
| G | 0.067m | 0.065m | 0.108m |

