technical data Small size conveyor chain Handling
Usage limit
1. Chain wear and elongation
To eliminate any play throughout the chain, measure the chain length with the chain tensioned to a certain extent. To minimize measurement error, measure the inside (L1) and outside (L2) of the rollers for 6 to 10 links to determine the reference dimension (L).
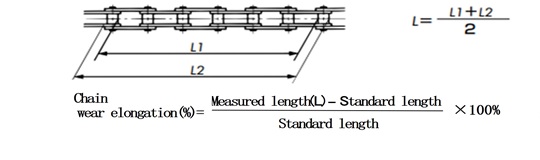
Reference length = Nominal chain pitch × Number of measured links
Replace the chain when its wear elongation exceeds 2%.
*Please also see the chain wear measurement scale, which allows you to check the pitch elongation limit at a glance.
Lambda Chain may run out of oil when the chain elongates by about 0.5%. Indicators of this are red Wear debris between the plates and poor bending.
This is the end of life.
2. R Roller
The life of the plate is reached when the outer circumference of the roller and the sliding part with the bushing wears out and the bottom surface of the plate starts to come into contact with guide channel.
When the plate begins to hit guide channel, frictional resistance increases, causing an increase in tension acting on the chain and a lack of motor output.
3. S Roller
When the rollers are worn down and develop holes or cracks, they have reached the end of their life.
4. Plate
When the plate slides directly on the transported object or on guide channel, the limit is when the plate's H dimension wears down to about 1/8 as shown in the diagram.

Figure 30. Plate width wear
5. Sprocket
When the sprocket wears down as shown in the diagram below (left), the chain gets caught in part A, making it difficult to release, causing the chain to vibrate.
The amount of wear tolerance varies slightly depending on the conveyor type and chain size, but if the chain is replaced when it has worn down to about 0.3mm to 1.0mm, it will not be damaged.
Also, if the sprocket is worn in the tooth width direction as shown in the diagram below (right), the shaft is not centered correctly and should be corrected.
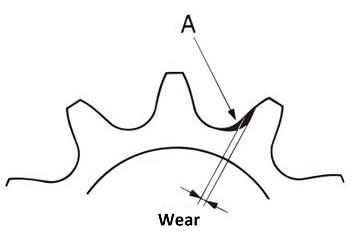

Figure 32. Sprocket tooth wear

